- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Anchor suture fixation for treatment of inferior patellar pole fractures better than traditional methods
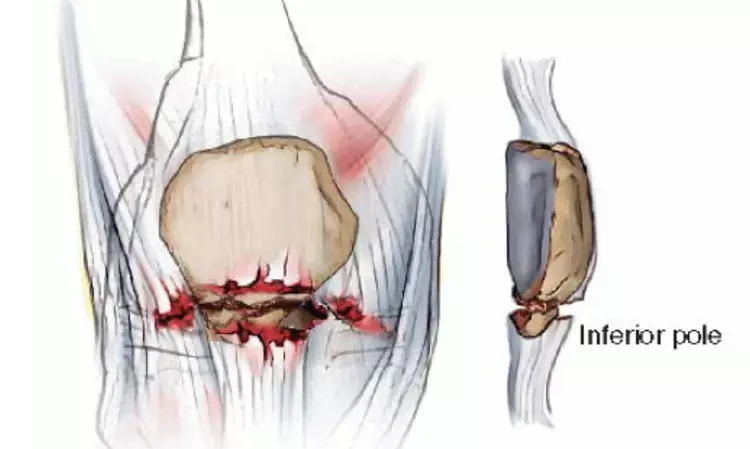
Anchor suture fixation for treatment of inferior patellar pole fractures better than traditional methods finds a new study by researchers.The findings of the study have been published in the journal Orthopaedic Surgery.
Jia Xie, Yu Fu et al conducted a retrospective study on treatment of inferior patellar pole fractures at the Second Hospital of Anhui Medical University and Hefei Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, China.
Patients with distal pole fractures of the patella have a disrupted extensor mechanism, which results in considerable functional disability. The ideal method should comply with three crucial demands: it should aid in reduction of the fracture, provide stable fixation and enable early rehabilitation.
Various methods have been introduced to fix distal patellar pole fractures, including tension band wiring, separate vertical wiring, the use of a basket plate, wiring through cannulated screws, and partial patellectomy, and each of these techniques has characteristic advantages and disadvantages.
The modified anterior tension band technique using Kirschner wire (K-wire) is one of the most common methods. Patients frequently complain of discomfort secondary to prominent hardware, leading to high rates of removal of hardware (ROH). Thus, revision surgery with K-wire removal becomes necessary in up to 65% of cases.
A novel technique that employs the application of two or three anchors to the patella and reattachment of the distal fragments together with the patellar tendon.
This study aims to quantify clinical and postoperative functional outcomes and to identify postoperative complications in a cohort of patients who were treated with non-absorbable braided suture fixation for distal pole fractures of the patella. These patients were then compared to a control group of patients who were treated for distal pole fractures of the patella using Kirschner wire.
Inclusion criteria: (i) diagnosed as distal pole avulsion fractures of the patella on CT or X-rays; (ii) accepted anchor and Krackow-"8" suture fixation (AS) and K-wire fixation; (iii) complete follow-up data; and (iv) retrospective study. Excluded criteria: (i) patients with other types of patella fractures; (ii) open fractures; (iii) no history of surgery in the affected limb; and (iv) patients who were unable to understand the items on the questionnaire.
Twenty-eight eligible patients with distal pole patella fractures were reviewed retrospectively. The anchor and Krackow-"8" suture fixation (AS group) was applied in 10 patients and 18 patients underwent K-wire fixation (K-wire group). The average age of patients was 46.000 +/-19.476 years in the AS group and 47.556 +/- 15.704 years in the K-wire group, with comparable demographic characteristics. All patients underwent regular follow-up the operative data and postoperative functional and clinical outcomes were recorded. Complications were recorded by clinical and radiographic assessment. Bostman patellar fracture functional score was used to evaluate knee function.
In the novel method - Two suture anchors (TwinFix Ti 5.0 mm, Smith Nephew, London, UK) and Krackow-"8" suture were inserted in the proximal patellar fracture fragment. Three equal portions of proximal patellar fracture, with anchors placed in the decile points. Four equal portions distal to the fracture, with the Ultrabraid suture running through the corresponding point. The use of Tauting wire to replace fracture reduction. Ultrabraid sutures were sutured using "8" sutures over the patellar surface. The distal patellar fragment and the patellar tendon are sutured using Krakow technique sutures. Standard rehabilitation protocol was followed post operatively.
Results:
• The mean follow-up was similar for the AS and the K-wire groups (P > 0.05).
• The incision length of AS group was significantly smaller than that of K-wire group (P < 0.05). Mean incision length was 5.350 +/- 0.851 cm (range, 4 -7 cm) in the AS group and 11.722 +/-1.602 cm (range, 9 -14 cm) in the K-wire group (P < 0.05).
• The final follow-up on the range of motion of the knee: the average extension lag was similar in two groups (P > 0.05); flexion and flexion–extension angle was slightly better in the AS group than in the K-wire group.
• The Bostman patella fracture functional score of AS group were better than K-wire group at 3 and 6 months after operation. The sixth month after surgery, the score was 28.300 +/- 2.214 (range, 23 - 30) points in the AS group and 24.667 +/- 1.970 (range, 21 - 27) points in the K-wire group (P < 0.05).
• Four kinds of postoperative complications were seen in two groups – infection , non- union, implant failure & re-operation surgery.
• One patient (10%) in the AS group and two patients (11.1%) in the K-wire group had infections.
• Two (11.1%) cases of nonunion in group K and three patients (16.7%) required re-operation: one due to infection and two due to early implant failure.
• In the AS group, all distal pole fractures of the patella showed bony union, without loosening, falling, pulling out and nonunion of the fractures 6 months after operation.
The authors concluded that Anchor and Krackow-"8" suture fixation is an easily executed surgical procedure that can significantly reduce incision length and achieve better surgical outcomes than traditional procedures with regard to postoperative complications, knee function and without requiring a second operation. This technique is an effective operation method for the treatment of inferior patellar pole fractures.
Anchor and Krackow-"8" Suture for the Fixation of Distal Pole Fractures of the Patella: Comparison to Kirschner Wire.
Jia Xie1† , Yu Fu1,2† , Jun Li1 , Hao Yu1 , Yong Zhang1 , Juehua Jing.
DOI: 10.1111/os.13124
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


