- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Artificial Intelligence promising for diagnosing hip fracture from hip radiographs: JAMA
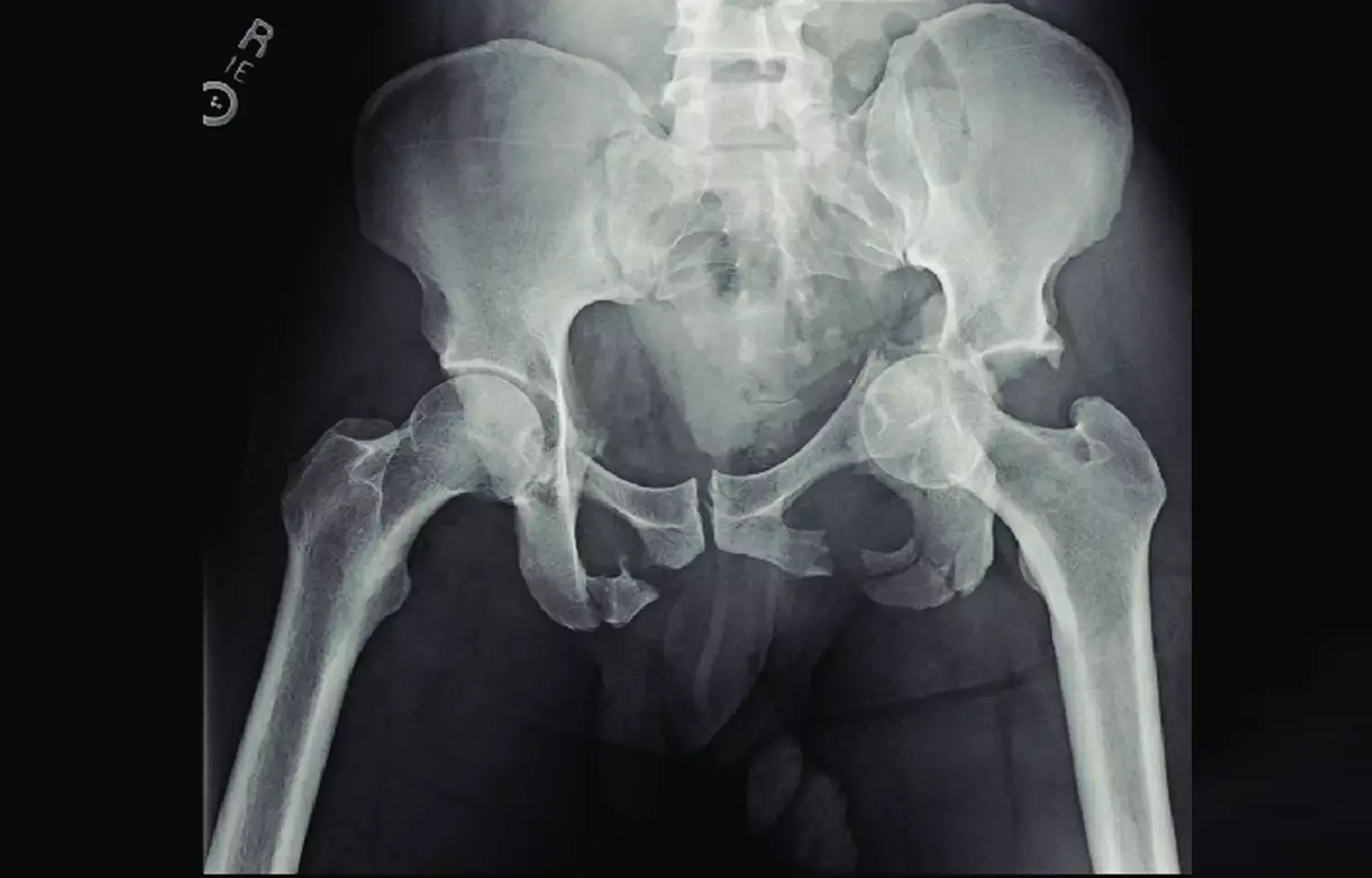
A recent systematic review and meta-analysis by Johnathan Lex and team suggests that there is potential for Artificial intelligence (AI) in the diagnositic process of hip radiographs. The findings of this study were published in the Journal of American Medical Association.
Strong models made possible by artificial intelligence can be used to construct clinical diagnostic and prognostic tools for hip fractures; however, the effectiveness and potential consequences of these recently established algorithms are yet unclear. In order to compare the efficacy of AI algorithms built to detect hip fractures on radiography and determine postoperative clinical outcomes after hip fracture surgery to existing procedures, this study was carried out.
Using the databases for Embase, MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Library, a thorough evaluation of the literature was conducted for all publications released up through January 23, 2023. To find any more pertinent papers, a manual reference search was also done on the listed articles. Included were studies using machine learning (ML) models to diagnose hip fractures from radiographs of the hip or pelvis or to forecast any postoperative patient outcome following hip fracture surgery.
The key findings of this study were:
A total of 39 papers that satisfied all requirements and were included in the study employed AI models in 18 (46.2%) of them to identify hip fractures on plain radiographs and in 21 (53.8%) of them to forecast patient outcomes after hip fracture surgery.
For training, validating, and testing ML models specific to diagnostic and postoperative outcome prediction, respectively, a total of 39 598 plain radiographs and 714 939 hip fractures were employed.
The most likely results were mortality and length of hospital stay.
In comparison to doctors, the OR for diagnostic mistake of ML models for hip fracture radiographs on pooled data analysis was 0.79.
The average (SD) sensitivity, specificity, and F1 score for the ML models were 89.3% (8.5%), 87.5% (9.9%), and 0.90, respectively (0.06).
In conclusion, when it came to identifying hip fractures, artificial intelligence performed on par with experienced radiologists and surgeons. The existing applications of AI for outcome prediction, however, do not appear to offer a significant advantage over multivariable predictive statistics.
Reference:
Lex, J. R., Di Michele, J., Koucheki, R., Pincus, D., Whyne, C., & Ravi, B. (2023). Artificial Intelligence for Hip Fracture Detection and Outcome Prediction. In JAMA Network Open (Vol. 6, Issue 3, p. e233391). American Medical Association (AMA). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3391
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


