- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Autologous PRP injection may benefit in acute ankle sprains by early return to activity and sports: study
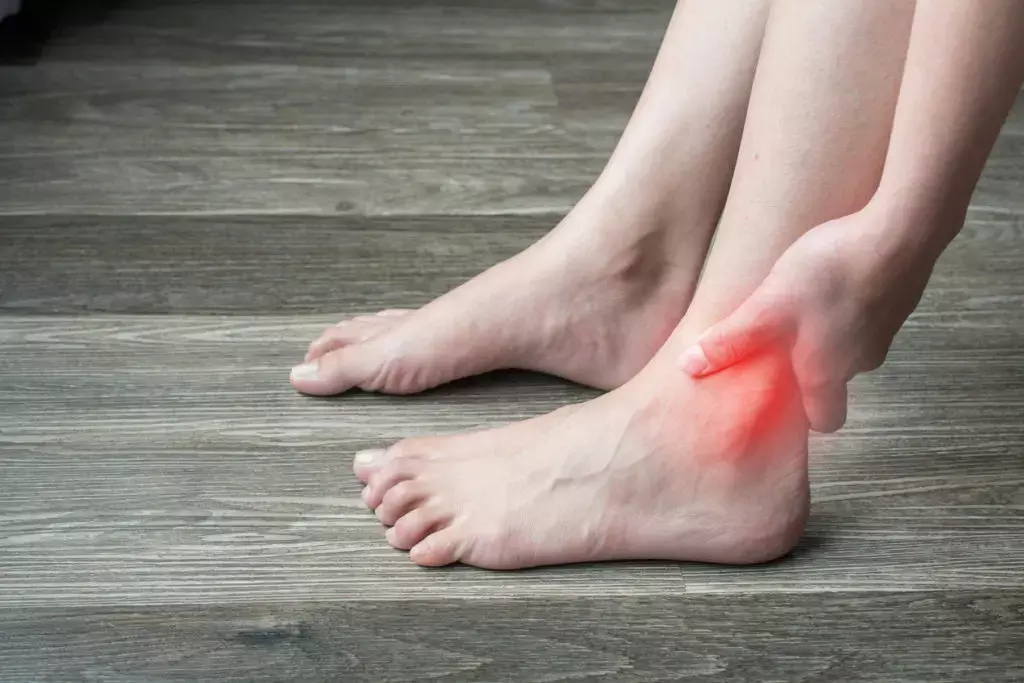
Lateral ankle sprains are common among active individuals and, if not managed properly, can result in recurrent sprains, chronic instability, and post-traumatic ankle osteoarthritis. Standard treatment includes physical therapy and a brief period of rest, followed by early functional rehabilitation. Autologous platelet-rich plasma, which is rich in growth factors, has demonstrated promising healing responses in acute ankle sprains.
Sumit Banerjee et al conducted a systematic review to assess the current evidence regarding the efficacy and adverse events associated with autologous PRP injection in acute ankle sprain injuries.
The authors conducted an electronic search across PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane Library using specific keywords. Eligible studies comprised prospective or retrospective comparisons of autologous PRP injection versus control for acute ankle sprain injuries reported in English.
The key findings of the study were:
• Three randomized controlled trials and one prospective comparative study met the inclusion criteria, involving 85 ankle injuries in 84 autologous PRP injection groups and 57 ankle injuries in 56 patients in the control group.
• Autologous PRP injection provided superior short-term pain relief, functional outcomes, and an earlier return to activity and sports, as well as improved radiological outcomes compared to the control group. However, during the follow-up period, both groups exhibited comparable results in terms of Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores and functional outcomes, with no reported adverse events.
• A meta-analysis of limited data for VAS and American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society scores demonstrated comparable outcomes between the two groups.
The authors concluded – “This systematic review of four studies has shown that there is a definite improvement in pain as evaluated by VAS score and functional outcome in the short term, which is translated to the early return to activity and sports in the PRP injection group than control; however, in due course of follow-up results were equivocal for both the groups without a short- or long-term adverse event related to PRP injection. However, we need multicentric RCTs with a larger population to substantiate the result, establish the efficacy of PRP, and look for long-term outcomes.”
Further reading:
Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Ankle Sprain: A Systematic Review of Literature with Limited Meta-Analysis Sumit Banerjee et al Indian Journal of Orthopaedics (2025) 59:910–919 https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-025-01418-1
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


