- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bisphosphonates Linked to Short-Term Pain Reduction in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Study
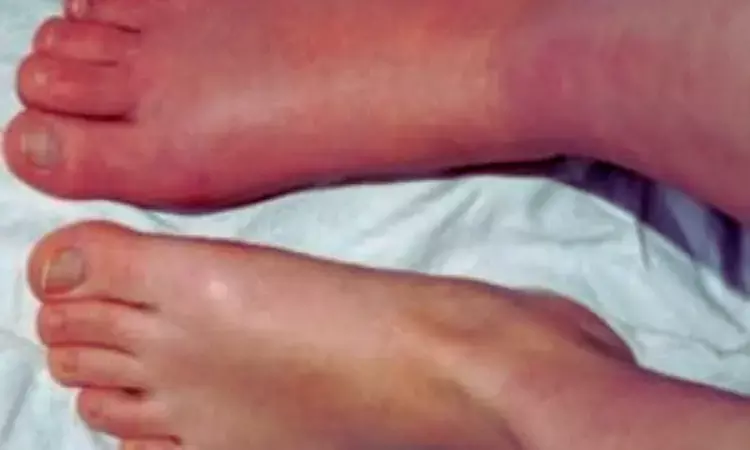
Australia: A new systematic review and meta-analysis has revealed that bisphosphonates may reduce pain in complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) in the short term (greater than 4 weeks up to 3 months). However, they appear less effective in the immediate (≤4 weeks) and medium-term (greater than 3 to 6 months). Treatment was also associated with an increased risk of adverse events, particularly arthralgia and myalgia.
- Bisphosphonates showed little to no reduction in pain during the immediate period of four weeks or less.
- A modest decrease in pain intensity was observed in the short term, between more than four weeks and three months, which was the primary assessment time point.
- Pain relief benefits diminished in the medium term (three to six months), with no meaningful difference compared with placebo.
- Evidence on long-term pain outcomes beyond six months was highly uncertain.
- Bisphosphonate treatment was associated with a higher risk of adverse events than placebo.
- Musculoskeletal side effects, particularly joint pain and muscle pain, were among the most frequently reported adverse events.
- The overall certainty of the evidence ranged from low to moderate due to variability among studies and methodological limitations.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


