- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Bone Mineral Density Declines More Rapidly in Adults With Cystic Fibrosis, finds study
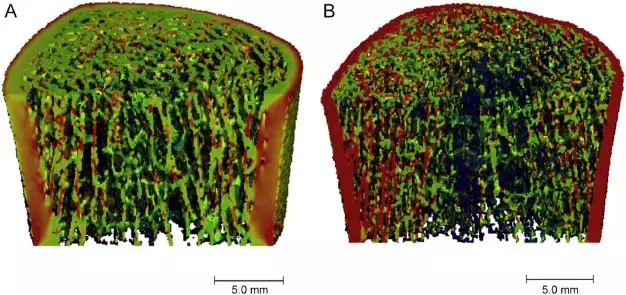
Bone mineral density declines more rapidly in adults with cystic fibrosis, according to a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
Improved survival in people with cystic fibrosis (pwCF) presents new complexities of care, including CF-related bone disease, a common complication in older pwCF. The trajectory of bone loss with age in this population remains unclear. The objective of this study was to estimate the average rate of change in bone mineral density (BMD) in adults with CF.
This retrospective study included adults with CF, aged 25-48 years, followed between January 2000 and December 2021. Subjects with at least one dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan were included. Scans obtained post-transplantation, after the initiation of bisphosphonates or cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulator therapy were excluded. The primary outcome was BMD (g/cm2) at the lumbar spine (LS) and femoral neck (FN). A linear mixed-effects model with both random intercept and random slope terms was used to estimate the average annual change in BMD.
Results: A total of 1502 DXA scans in 500 adults (average age 28.4y) were included. There was a statistically significant annual decline in BMD of -0.008 gm/cm2/year (95% CI -0.009, -0.007) at the FN and -0.006 gm/cm2/year (95% CI -0.007, -0.004) at the LS. Relative to BMD at age 25, there was a -18.8% decline at the FN by age 48 years and a -11% decline at the LS. Pancreatic insufficient (PI) subjects had a faster rate of decline in BMD compared to pancreatic sufficient (PS) subjects. After adjusting for markers of disease severity, the annual rate of decline remained significant. Individuals with CF experience bone loss at an age when it is not anticipated, thereby entering early adulthood, where further bone loss is inevitable especially with the decrease in estrogen during menopause, with suboptimal BMD. As the CF population ages, it will become very important to consider interventions to maximize bone health.
Reference:
Jad R, Ma X, Stanojevic S, et al. Longitudinal changes in bone mineral density in adults with cystic fibrosis. J Bone Miner Res. Published online September 2, 2024. doi:10.1093/jbmr/zjae139.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


