- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Concomitant Ulnar Styloid Fractures can be left untreated while treating Distal Radius Fractures with surgical fixation
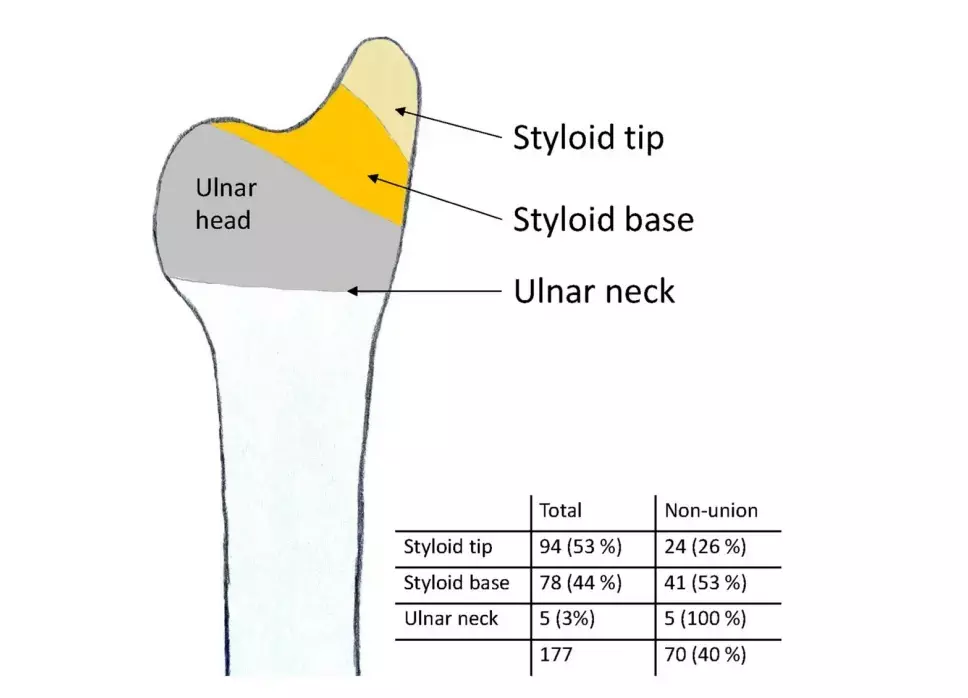
Distal radial fractures (DRFs) are one of the most common fractures and are associated with concomitant ulnar styloid fractures (USFs) in up to 65% of cases.
Although surgical fixation of DRFs has become more common since the introduction of volar locking plates, there is no consensus on how to treat concomitant USFs. It is also unclear whether an associated USF affects the outcome of a DRF. When unstable DRFs are treated surgically, any associated USF is most commonly left untreated.
Stale Orstavik Clementsen et al conducted a study to evaluate the effect of a concomitant USF on outcome after surgical stabilization of a DRF. Investigation performed at Akershus University Hospital, Lorenskog, Norway.
Data from 2 randomized controlled trials on the treatment of unstable DRFs were pooled. The effect of a USF on the QuickDASH, EQ-5D, pain, and range of motion at 2 years was evaluated.
Key findings of the study:
• Two hundred and eighty-one patients were included; 177 (63%) had an associated, untreated USF.
• The mean patient age was 55 years (range, 19 to 70 years), and the majority of the patients were female (219, 78%).
• An unadjusted analysis demonstrated no significant difference in functional or patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) at 2 years between patients with or without a concomitant USF.
• When controlling for confounding factors, the presence of a USF did not predict change in any of the PROMs from baseline to 2 years.
• A concomitant USF also did not predict change in grip strength or range of motion, except for a small effect on extension (-4.10; 95% confidence interval, -7.50 to -0.80; p = 0.02), which probably does not have clinical relevance.
The authors concluded that – “The main strengths of the study are the large sample size, the prospective design, and low loss of follow-up. We found that USFs in combination with DRFs did not affect PROMs, range of motion, or grip strength. Furthermore, nonunion of the USF did not affect clinical outcome. We recommend that concomitant USFs with stable distal radial ulnar joints be left untreated when treating a DRF with surgical fixation.”
Level of Evidence: Prognostic Level I.
Further reading:
The Effect of Ulnar Styloid Fractures on Patient-Reported Outcomes After Surgically Treated Distal Radial Fractures
Stale Orstavik Clementsen, Rune Bruhn Jakobsen et al
JBJS Open Access 2022:e22.00021.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.OA.22.00021
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


