- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Epidural Corticosteroid Injections may reduce Sciatica pain and disability
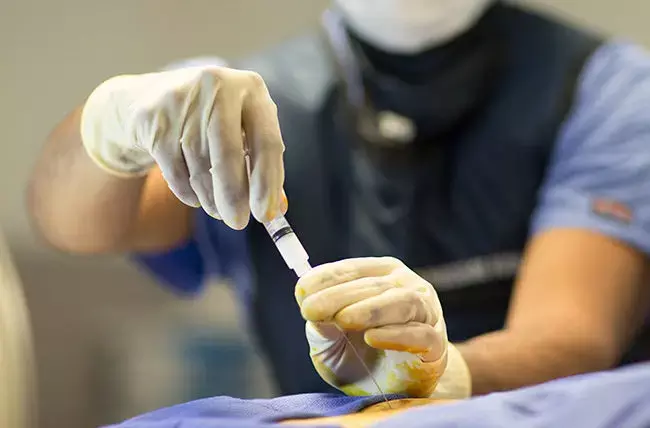
In a recent study based on moderate-quality evidence from 25 placebo-controlled trial researchers have found that epidural corticosteroid injections are effective for reducing leg pain and disability in sciatica. The details of the study were published in the Spine journal on November 1, 2020.
Traditional treatment approach for sciatica includes pharmacological, non-surgical and surgical treatment is a typically the first-line treatment but the evidence to support their use is limited. Previous systematic reviews investigated the effects of epidural corticosteroid injections compared with placebo injection in patients with sciatica. However, the overall quality of evidence found by these systematic reviews varies between moderate and high which suggest that future trials may change the conclusions. For this purpose, the researchers conducted a Abridged Cochrane Systematic Review and Meta-analysis investigating the efficacy and safety of epidural corticosteroid injections compared with placebo injection in reducing leg pain and disability in patients with sciatica.
They evaluated 25 clinical trials (from 29 publications) and a total of 2470 participants from placebo-controlled randomized trials investigating epidural corticosteroid injections in patients with sciatica were included. The major outcome analyzed were leg pain intensity and disability. Adverse events, overall pain, and back pain intensity were also analyzed as a secondary outcome. Researchers grouped similar trials according to outcome measures and their respective follow-up time points and determined Short-term follow-up (>2 weeks but ≤3 months) as primary follow-up time point due to the expected mechanism of action of epidural corticosteroid injection.
At the end of the analysis, they found epidural corticosteroid injections were probably more effective than placebo in reducing short-term leg pain with the mean difference of −4.93 and for short-term disability, it was −4.18. They also found epidural corticosteroids were slightly more effective in reducing short-term overall pain when compared with placebo with a mean difference of −9.35. They observed minor adverse events (i.e., without hospitalization) after both the treatments. Limitation of the trial was the quality of evidence which was at best moderate mostly due to problems with trial design and inconsistency.
The authors concluded, "A review of 25 placebo-controlled trials provides moderate-quality evidence that epidural corticosteroid injections are effective, although the effects are small and short-term. There is uncertainty on safety due to very low-quality evidence".
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


