- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Erythropoietin use linked to risk of hip fractures in dialysis patients: Study
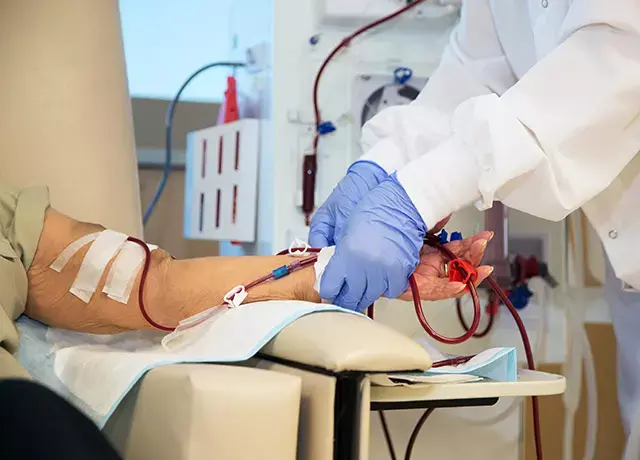
According to a recent study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, researchers have observed that erythropoietin treatment (EPO) treatment can be an independent risk factor for hip fractures in hemodialysis patients.
Erythropoietin (EPO) is the primary regulator of bone marrow erythropoiesis. Mouse models have provided evidence that EPO also promotes bone remodeling and that EPO‐stimulated erythropoiesis is accompanied by bone loss independent of increased red blood cell production.
EPO has been used clinically for three decades to treat anemia in end‐stage renal disease, and notably, although the incidence of hip fractures decreased in the United States generally after 1990, it rose among hemodialysis patients coincident with the introduction and subsequent dose escalation of EPO treatment.
Given this clinical paradox and findings from studies in mice that elevated EPO affects bone health, the authors, Sukanya Suresh and colleagues from the Molecular Medicine Branch, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA examined EPO treatment as a risk factor for fractures in hemodialysis patients.
Relationships between EPO treatment and hip fractures were analyzed using United States Renal Data System (USRDS) datasets and Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web‐enabled Network (CROWNWeb) datasets.
Fracture risks for patients treated with <50 units of EPO/kg/week were compared to those receiving higher doses by multivariable Cox regression.
The following findings were seen-
a. Hip fracture rates for 747,832 patients increased from 12.0 per 1000 patient to 18.9, then decreased to 13.1 in the later years.
b. Concomitantly, average EPO doses increased from 11,900 units/week to 18,300 in, then decreased to 8,800.
c. During this time, adjusted hazard ratios for hip fractures with EPO doses of 50–149, 150–299, and ≥ 300 units/kg/week compared to <50 units/kg/week were 1.08 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01–1.15), 1.22 (95% CI, 1.14–1.31), and 1.41 (95% CI, 1.31–1.52), respectively.
d. Multivariable analyses of 128,941 patients in CROWNWeb datasets replicated these findings.
Therefore, the authors concluded that "this study implicates EPO treatment as an independent risk factor for hip fractures in hemodialysis patients and supports the conclusion that EPO treatment may have contributed to changing trends in fracture incidence for these patients during recent decades."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


