- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
High sensitivity cardiac troponin levels tied to disease activity in inflammatory arthritis
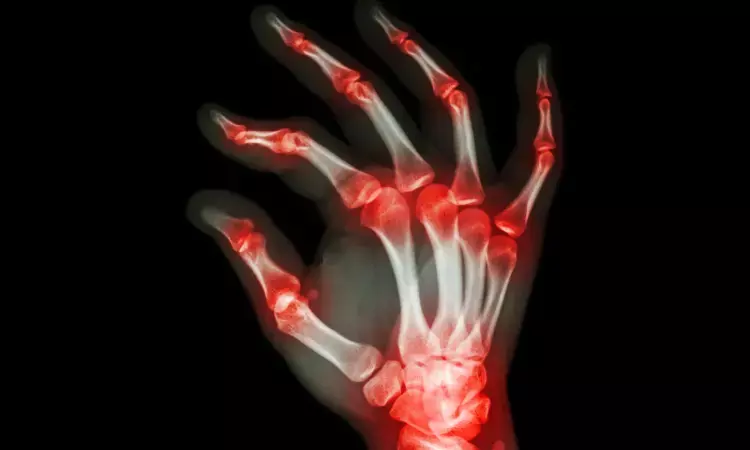
Norway: According to the findings of a new study published in PLOS ONE, High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T(hsTnT) levels in patients of inflammatory arthritis (IA) have a positive correlation with disease activity markers like swollen joints and serum levels of tumour necrosis factor.
The hsTnT is a cardiovascular disease marker, and studies say that it is a potentially useful marker of inflammation in the body, including the joints.
HsTnT is elevated in inflammatory arthritis (IA) patients due to unclear mechanisms. However, the significant role attributed here is systemic inflammation and atherosclerotic plaques (instability and rupture).
hsTnT is not only a reflector of the acute coronary syndrome but also chronic atherosclerotic disease and localized myocardial necrosis. It correlates with coronary plaque burden.
Considering this background and increasing CHD risk in inflammatory arthritis (IA) patients with the possible association of myocardial injury and inflammation, the researchers hypothesized that.
“hsTnT levels match up with systemic inflammatory and clinical markers for IA disease activity and can be influenced by antirheumatic therapy.”
The study summary includes the following:
- One hundred fifteen patients had active Inflammatory arthritis.
- Sixty-four patients had rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 31 psoriatic arthritis and 20 patients had ankylosing spondylitis, before and after using methotrexate (MTX) alone or tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) with or without MTX co-medication (TNFi±MTX).
- The patients initiating TNFi were unsuccessfully treated with MTX monotherapy.
- There was a positive correlation of hsTnT with Physicians’ Global Assessment Score of disease activity in the total patient cohort.
- In the RA group, there was a positive correlation between hsTnT and swollen joints.
- The Median hsTnT level at baseline was 5.0 ng/L, and there was no significant change at the 6-week visit and 6-month visit with values of 6.0 ng/L with either antirheumatic therapy.
The study’s strengths were the comprehensive characterization of the patient population and the design, while limitations include sample size and observational design.
To conclude, hsTnT levels are related to markers for inflammatory arthritis (IA) disease activity, and there is no improvement during six months of antirheumatic treatment.
Further investigations are warranted for the hsTnT role in cardiovascular risk prediction in IA patients.
Nguyen THP et al. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T is associated with disease activity in patients with inflammatory arthritis. PLoS One. 2023 Feb 10;18(2):e0281155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281155.
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


