- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Is Gastrocnemius Recession Surgery best surgical treatment for Planter Fasciitis foot?
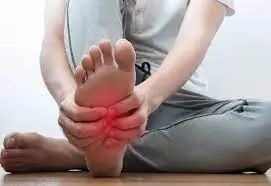
Heel discomfort that manifests in an outpatient situation is most frequently due to plantar fasciitis. It is deleterious, because it causes foot pain, ambulation problems, exercise restrictions, and the inability to support one's weight. Isolated gastrocnemius tightness has been found to be positively associated with the progression of plantar fasciitis and other foot-related pathological conditions. Around 10% of the patients with plantar fasciitis were reported to show no response to the conservative treatments like - rest, muscle-strengthening protocols, non-steroidal antiinflammatory stimulants, massage, heel pads, steroid, and platelet-rich plasma injections.
A systematic and meta-static review was conducted by Abhijit Bandyopadhyay et al to analyze the correlation between isolated gastrocnemius contracture and plantar fasciitis and the effectiveness of gastrocnemius recession surgery in the treatment of plantar fasciitis.
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were followed to conduct this meta-analysis. A literature search was carried out on the following databases, including Google Scholar, PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane databases with the appropriate medical subject headings (MeSH) to identify the eligible articles.
Key findings of the study were:
• A total of 13 studies were included in this meta-analysis out of 721 articles.
• In this study, there is a significant difference in chronic plantar fasciitis outcome when comparing experimental and control (RR: 0.02; 95% CI: 0.01 to 0.05; P< 0.001)
• There is a significant difference in pain scale outcome when comparing pre-treatment and post-treatment (RR: 3.25; 95% CI 1.44 to 7.32; P=0.004< 0.01).
• A significant difference in VAS scale outcome when comparing pre-treatment and post-treatment (RR: 2.58; 95% CI 1.52 to 4.38; P=0.0004< 0.01).
“In conclusion, the current systematic review and meta-analysis of gastrocnemius recession and proximal medial gastrocnemius release and other treatment measures for plantar fasciitis suggests that the improvement of ankle dorsiflexion, reduction in pain, and patient satisfaction are almost similar in all the treatment measures. Among the five treatment measures, gastrocnemius recession remains the best, followed by proximal medial gastrocnemius release” the authors concluded.
Further reading:
Isolated Gastrocnemius Contraction and Gastroc Recession Surgery in Case of Planter Fasciitis: A Systemic Review and Meta Analysis
Abhijit Bandyopadhyay et al
Indian Journal of Orthopaedics (2023) 57:1359–1375
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-00939-x
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


