- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Local administration of TXA effectively reduces postoperative blood loss in calcaneal fractures surgery
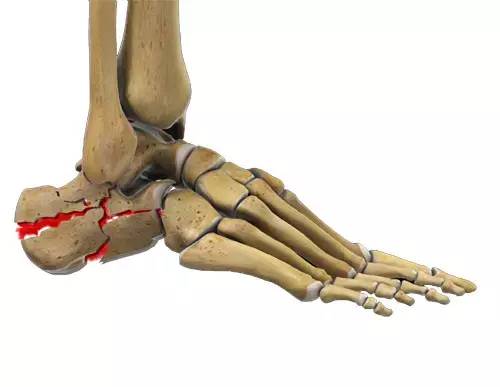
For closed, Sanders III-IV calcaneal fractures, open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) is the standard treatment. However, a large amount of perioperative blood loss is usually associated with the surgeries to repair calcaneal fractures as it is a cancellous bone with abundant blood supply, which increases the chance of blood transfusion and the associated risks to patients with calcaneal fractures. Moreover, the large amount of postoperative blood loss around the affected calcaneus will also increase the risk of wound complications.
Lang Zhong et al conducted a study to investigate whether local administration of tranexamic acid (TXA) is effective in postoperative blood loss reduction in surgeries for Sanders III–IV calcaneal fractures. The article has been published in Indian Journal of Orthopaedics.
Calcaneal fracture patients who underwent open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) via lateral approach with an L-shaped incision were included in the study.
53 patients were randomly divided into three groups, groups A (17), B (17) and C (19). Twenty milliliters of 10 mg/ml and 20 mg/ml TXA solution were perfused into the incision of patients in group A and group B, respectively. Twenty milliliters of saline were perfused into the incision of patients in group C as control. The volume of postoperative drainage, postoperative blood test, coagulation test, and wound complications were analyzed to evaluate the effectiveness of local administration of TXA on blood loss reduction.
Key findings of the study were:
• The amount of drainage at 24 and 48 h after the procedure was 110±170, 30±10 ml and 130±160, 20±17 ml for patients in group A and group B.
• The corresponding numbers for patients in group C were 360±320, 20±10 ml.
• The difference between group A and group C was statistically significant, so was the difference between group B and group C.
• No statistically significant difference was found between group A and group B.
• Postoperative blood test results revealed that the levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit were significantly higher in group A and group B when each compared to that of group C. In contrast, no difference was found between group A and group B.
• No significant difference was found between each experimental group and the control group in terms of platelet counts, prothrombin time (P.T.), activated partial prothrombin time (APTT), and wound complications.“
In the present study, we validated that local administration of TXA effectively reduced the postoperative blood loss in surgeries for Sanders III–IV types of calcaneal fractures without increasing the incidence of wound complications, suggesting the potential benefits of local administration of TXA in treatment for calcaneal fractures” the authors commented.
Further reading:
Effects of Local Administration of Tranexamic Acid on Reducing Postoperative Blood Loss in Surgeries for Closed, Sanders III–IV Calcaneal Fractures: A Randomized Controlled Study Lang Zhong , Yu Liu et al Indian Journal of Orthopaedics (2021) 55 (Suppl 2):S418–S425https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00417-2
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


