- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
MIPO more advantageous than ORIF in treatment of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: study
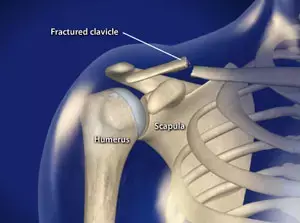
Wang et al conducted a study to evaluate the clinical efficacy and advantages of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures (DMCFs).
A retrospective case–control study was conducted involving 79 patients with DMCFs. Patients were divided into two groups based on the surgical technique: MIPO (n = 32) and Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) (n = 47). Key parameters—including operative time, intraoperative blood loss, incision length, complications, patient satisfaction, and functional recovery outcomes—were compared.
The key findings of the study were:
• Baseline characteristics were comparable between the two groups, including age (41.66 ± 11.32 years vs. 42.53 ± 11.18 years, p = 0.731), sex distribution (male/ female: 18/14 vs. 31/16, p = 0.383), BMI (23.24 ± 2.21 vs. 23.86 ± 1.74, p = 0.170), smoking history (25.0% vs. 29.8%, p = 0.641), alcohol use (12.5% vs. 21.3%, p = 0.316), hypertension (18.8% vs. 10.6%, p = 0.798), diabetes mellitus (15.6% vs. 14.9%, p = 0.929), injury mechanism (p = 0.406), AO/OTA fracture classification (p = 0.635), and Robinson classification (p = 0.536). No statistically significant differ¬ences were observed in any of these parameters.
• Compared to the ORIF group, the MIPO group demonstrated significantly shorter operative time (54.22 ± 5.14 min vs. 61.15 ± 6.01 min, p < 0.001), reduced intraoperative blood loss (45.44 ± 4.27 mL vs. 52.81 ± 6.60 mL, p < 0.001), and shorter incision length (6.42 ± 0.48 cm vs. 12.25 ± 1.60 cm, p < 0.001).
• Postoperative supraclavicular nerve injury was less frequent in the MIPO group (12.5% vs. 38.3%, p < 0.001) and patient satisfaction was higher (90.6% vs. 72.3%, p = 0.021).
• No significant differences were observed in functional outcomes, as assessed by the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) and Constant-Murley scores.
The authors concluded – “Both MIPO and ORIF are effective surgical options for the management of DMCFs. Although functional recovery outcomes were comparable between the two techniques, MIPO demonstrated clear advantages in terms of reduced surgical trauma, accelerated postoperative recovery, lower complication rates, and higher patient satisfaction. These findings support the wider clinical adoption of MIPO, particularly in healthcare settings that emphasize minimally invasive approaches and enhanced recovery protocols.”
Further reading:
Clinical outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the management of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: a case-control study
Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2025) 26:905
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-025-08995-0
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


