- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
New bone fracture fixation method could replace metal plates, with lesser complications: Study
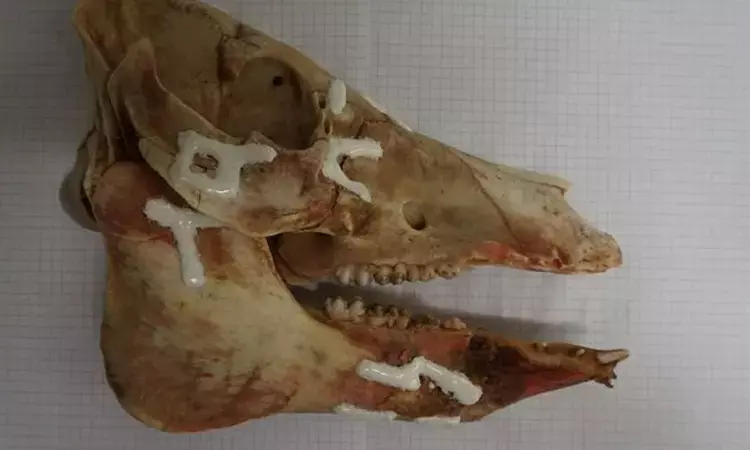
Sweden: A new biocompatible polymer-based composite material developed at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm could soon replace metal plates in treating difficult and unstable fractures. The newly-developed material is as strong as dental composites yet non-toxic.
The paper comprising of material and surgical method, published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, will be used in clinical studies in 2023 and 2024, with a focus on hand fractures.
Michael Malkoch, professor of fiber and polymer technology at KTH, says that the material and method, AdhFix, will enable customized plating for fixation of fractures with a more comfortable, less complicated recovery. Collarbone and rib fractures in particular are ideally suited for the proposed treatment, since such injuries are not easy to stabilize.
Metal plates cannot be easily customized in shape, and they tend to adhere to soft tissue, resulting in debilitating complications, says Malkoch. For example, researchers in the U.S. have found that nearly 64 percent of finger fractures treated with metal plates result in mobility complications.
The alternative surgical method, AdhFix, combines screws with a build-up of the polymer/hydroxyapatite composite instead. The composite is shaped in situ before being rapidly cured on-demand via high-energy visible-light-induced thiol-ene coupling chemistry.
Evaluations on human cadaver hands with proximal phalanx fractures show that AdhFix withstands the forces from finger flexing exercises. In models of in vivo femur fractures in rats, the methodology supported bone healing without degradation, adverse effects or soft-tissue adhesions.
"No fracture is the same as the other, this is one of the absolute advantages of the material," says Malkoch. "A surgeon can tailor the fixation plate according to the patient's bone shape and the structure of the fracture. The hospital also does not have to store metal plates."
Malkoch says the material and method also may be applied to veterinary care as well. Animals with metal plates are known to avoid going outdoors in cool temperatures because the metal conducts the cold differently than the KTH researchers' composite.
Reference:
The study titled, "Highly Customizable Bone Fracture Fixation through the Marriage of Composites and Screws," is published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
DOI: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.202105187
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


