- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Plantar Fascia Release combined with Calcaneal Decompression may improve resistant heel pain
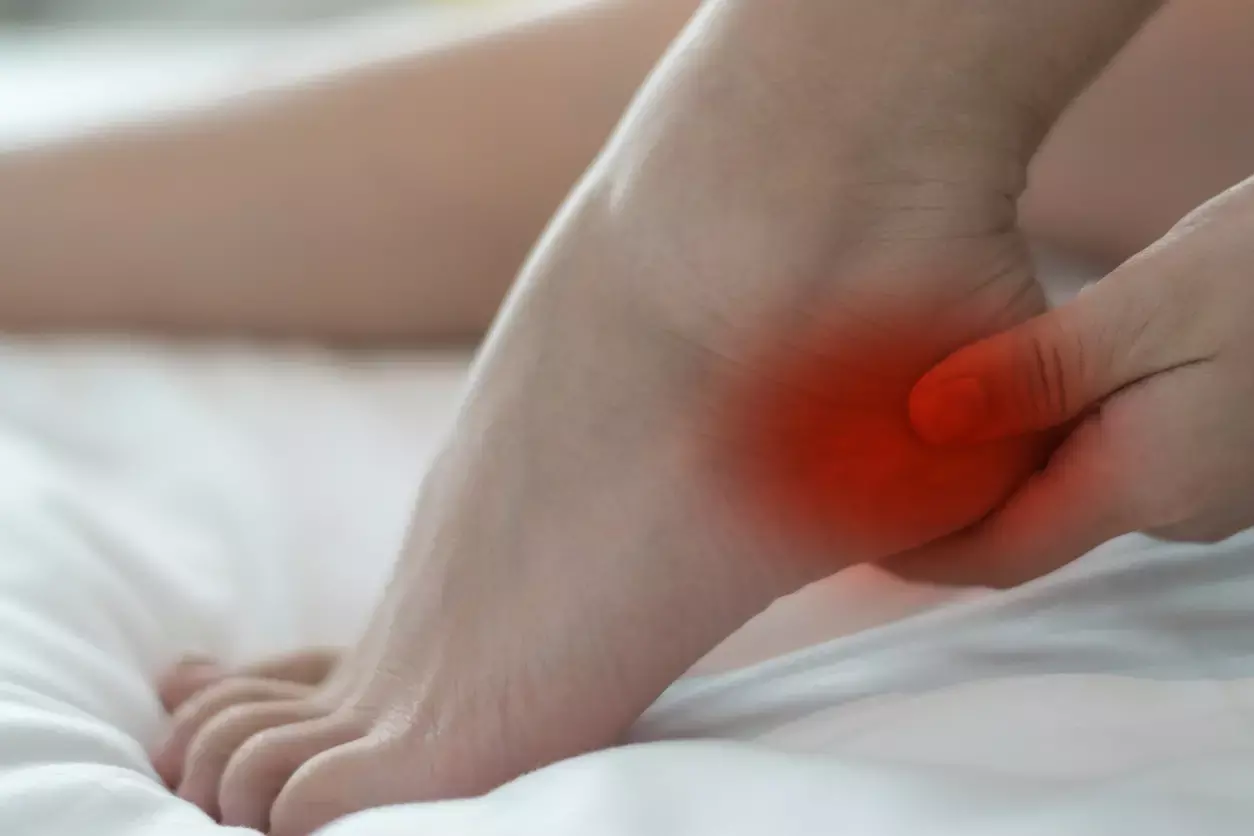
Istanbul, Turkey:
K. Karaytug et al. compared isolated percutaneous plantar fascia release by using a needle versus percutaneous plantar fascia release combined with calcaneal decompression in treatment of the patients with resistant heel pain.
The authors reviewed the prospectively recorded data of patients who treated and follow-up for resistant heel pain (treated more than 6 months with other treatment modalities) with a minimum 1-year follow-up.
Calcaneal drilling was performed under general or spinal anesthesia with the patient placed in the lateral decubitus position. Calcaneal decompression was performed percutaneously using a Kirschner wire under fluoroscopy with 3 to 6 drill holes in the inferior cortex.
Twenty patients were treated with plantar fascia release using a needle (group 1) and 21 patients were treated with a similar percutaneous release combined with calcaneal decompression (group 2). Functional outcomes were evaluated using visual analog scale (VAS) and Foot Function Index (FFI) pre- and postoperatively.
No significant differences were observed between both groups in terms of age (44.3 years in group 1 vs 46.8 years in group 2), gender (18 females and 2 males in group 1 vs 19 females and 3 males in group 2), body mass index (25.1 in group 1 vs 26.3 in group 2), and follow-up (14.6 months in group 1 vs 15.7 months in group 2).
The decrease in postoperative FFI (Foot Function Index) and VAS (Visual Analogue Scale) scores compared with preoperative VAS scores was statistically significant in both groups. However, improvement of FFI and VAS score was significantly higher in group 2 than group 1.
Although both methods are very effective in the treatment of persistent heel pain, the group 2 has a better improvement in functional scores than group 1 with a mean 15 months following the procedure.
The authors concluded that - percutaneous release of the plantar fascia in persistent heel pain enables patients to achieve satisfactory functional results. Calcaneal drilling is an effective method to increase the success rate and carries a low risk of complication. Although both methods are very effective in the treatment of persistent heel pain, the group 2 had a better improvement in functional scores than the group 1 within 15 months following surgery.
Further reading:
Comparison of the Isolated Plantar Fascia Release Versus Plantar Fascia Release Combined With Calcaneal Decompression in Management of the Patients With Resistant Heel Pain
Kayahan Karaytug, Serkan Bayram, Mehmet Ekinci, Onder Murat urmeydan, Sefa Giray Batibay.
The Journal of Foot & Ankle Surgery 61 (2022) 459−463
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2021.09.017
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


