- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Platelet-rich plasma may Improve mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome: Study
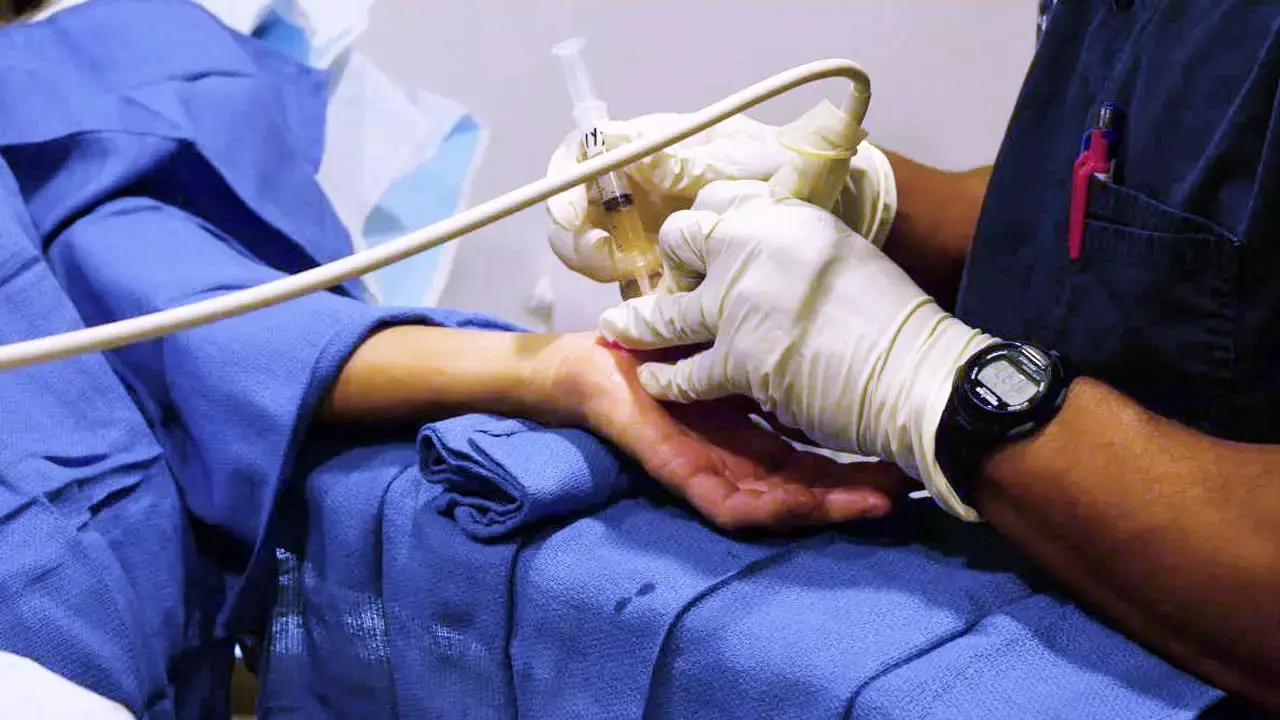
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common mono-neuropathy accounting for approximately 90% of peripheral entrapment neuropathies. Estimates of prevalence range from 4% up to 20% in the industrial populations. In a recent study, researchers have found that platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections improve pain scores, functional outcomes as well as cross-sectional area (CSA) measurements of the median nerve (MN) in patients with mild to moderate CTS. The study findings were published in the Journal of Orthopaedics on May 07, 2021.
Previous studies support the use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections for those with CTS undergoing non-operative management. However, data on the effect of PRP in either nerve conduction studies (NCS) or the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the MN in CTS remain unclear. Therefore, researchers of Ireland conducted a study to perform an updated systematic review with meta-analysis on trials focusing on patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs), NCS and CSA measurements of those who underwent PRP injection for mild to moderate CTS versus a control.
In this systematic review & meta-analysis, researchers reviewed MEDLINE, EMBASE and Scopus databases in June 2020 and included a total of 8 prospective studies on the use of PRP in the non-operative management of CTS versus control with a mean follow-up time of 3.9 months. They included data of 404 patients from 8 studies for the analysis. They used Qualitative statistical analysis for systemic analysis and Review Manager for meta-analysis.
Key findings of the study were;
- Upon analysis, the researchers found that the use of PRP in CTS improved symptoms and functional outcomes compared with controls.
- They also found that the PRP resulted in significantly smaller CSA (9.65 mm2) than controls (9.95 mm2).
- However, they found no corresponding improvement in either motor (distal motor latency: 4.9 m/s verses 5.1 m/s) or sensory results (sensory nerve conduction velocity:33.5 m/s verses 34.3 m/s)of NCS with PRP.
The authors concluded, "This study indicates that there may be a potential role for the use of PRP in the non-operative management of mild to moderate CTS results in improvements in pain scores, functional outcomes as well as CSA measurements of the MN at short-term follow-up. However, PRP does not result in improvements in NCS."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


