- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sclerotherapy comparable to conventional curettage and bone grafting for aneurysmal bone cyst
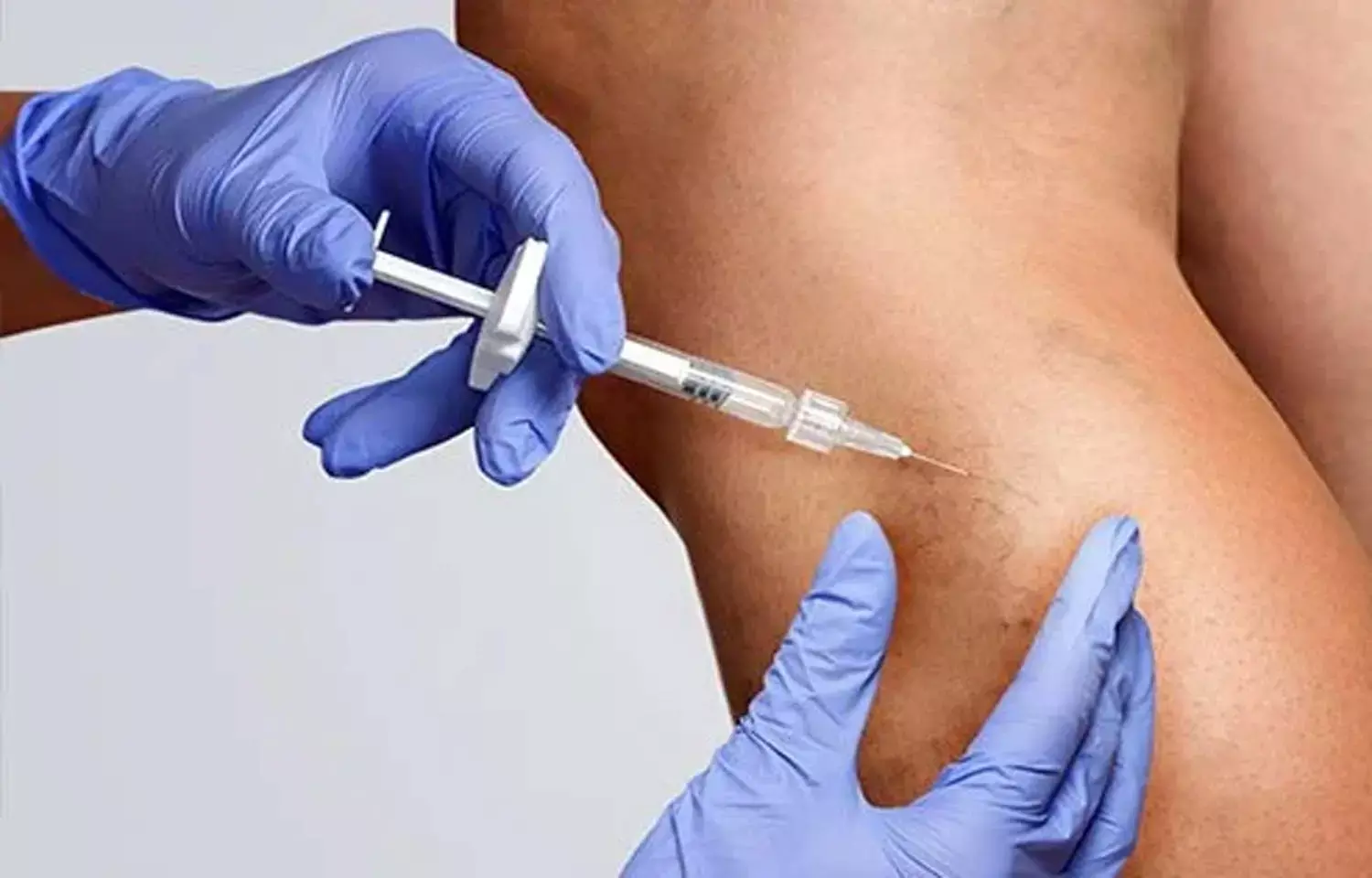
Researchers from a recent study have found out that percutaneous sclerotherapy using polidocanol is a highly effective, cost efficient and safe treatment option with good cosmesis and reduced morbidity when compared to the conventional curettage and bone grafting procedure.
The study is published in the Journal of Orthopaedics.
The standard treatment of Aneurysmal bone cyst is curettage and grafting and is associated with high morbidity. Hence minimal invasive alternative treatment methods such as sclerotherapy are gaining much popularity. Though sclerotherapy has been attributed to reasonable cure rates, undetermined tissue diagnosis often impedes with initiation of treatment.
Therefore, Dominic Puthoor and associates from the Orthopaedic Oncologist, Professor and Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics, Amala Institute of Medical Sciences, India carried out this research to examine if sclerotherapy with polidocanol based on clinic-radiological picture is comparable with the standard intralesional curettage and bone grafting. Attempting biopsy and treatment simultaneously based on the clinico-radiological presentation makes this study unique.
The authors divided 48 patients into two treatment groups. Group 1 treated with percutaneous sclerotherapy using polidocanol and group 2 those treated with extended curettage and bone grafting.
Time to healing and recurrence, pain relief, and radiological outcome using modified Neer's criteria for the radiological healing of the bone cysts were assessed. 31 patients from Group 1 and 17 from Group 2 were available for study. The minimum follow-up was 2 years.
The key findings highlighted were-
- At last follow-up, 100% in Group 1 and 82% in Group 2 had achieved complete healing and there was no statistical difference in outcome at 24 months (p = 0.255).
- Complications in Group 1 were injection site necrosis, pain and hypopigmentation, all of which resolved spontaneously.
- In Group 2, three patients had recurrence.
- Despite similar healing rates, we found higher incidence of clinically pertinent complications, poor functional outcomes and increased cost of treatment associated with intralesional excision.
- Three cases were excluded from sclerotherapy group as the final diagnosis turned up to be secondary ABC.
Hence, it was concluded that "percutaneous sclerotherapy using polidocanol is a highly effective, cost efficient and safe treatment option with good cosmesis and reduced morbidity. In this study, we found comparable outcomes for both treatment methods however this will require confirmation in larger studies."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


