- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Serum Procalcitonin Shows Promise but Limited Sensitivity for Diagnosing Pediatric Osteomyelitis: Study
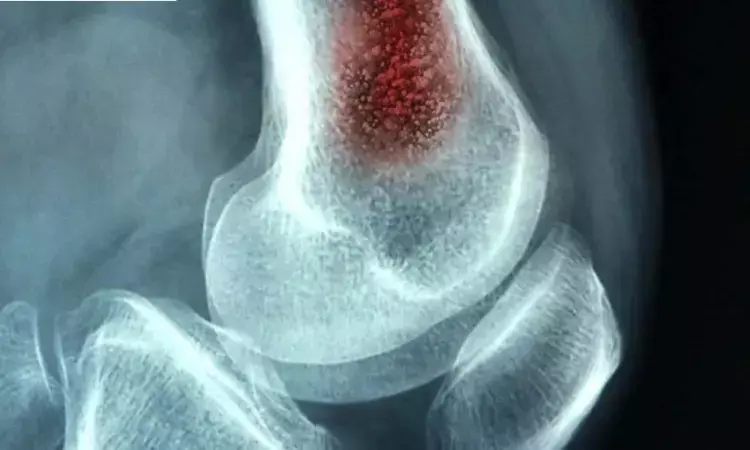
Researchers believe that serum procalcitonin (PCT) may turn out to be a helpful biomarker in the diagnosis of pediatric osteomyelitis, even when its sensitivity is low. A recent study by Han Qi and colleagues has tried to determine the sensitivity, specificity, and predictive utility of PCT for the diagnosis of osteomyelitis in children through systematic review with meta-analysis of relevant literature. This study was published in BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.
An elaborate computer-based search was undertaken for studies that considered PCT for the diagnosis of pediatric osteomyelitis. Accordingly, records were screened and selected according to PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Review Manager software 5.3, Meta-disc software 1.4, STATA 12.0, and R 3.4 software were used for statistical analyses.
Key Findings
• A total of five studies were included in the analysis, encompassing 148 children diagnosed with osteomyelitis who were tested for bacterial cultures in PCT.
• The diagnostic meta-analysis revealed a pooled sensitivity of 0.58 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.49 to 0.68) and a pooled specificity of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.90 to 0.93) for PCT in diagnosing pediatric osteomyelitis.
• The area under the curve (AUC) for PCT in the diagnosis of osteomyelitis in children was 0.80, indicating a good level of diagnostic accuracy.
• The Deeks’ regression test for asymmetry showed no publication bias (P = 0.90).
The results indicate that the sensitivity of PCT is relatively low against high specificity, which suggests it is good at correctly excluding those without the disease but less good at picking up most of those with the disease. This therefore raises the potential utility of PCT as a part of a larger diagnostic strategy rather than as a standalone test for pediatric osteomyelitis.
This is a comprehensive literature review for the application of PCT in diagnosing pediatric osteomyelitis. Although PCT may represent an interesting biomarker, low sensitivity indicates that the use of the marker by itself is not plausible; therefore, it would have to be combined with other diagnostic tools. Further studies in bigger populations are needed to prove the accuracy of PCT for this indication.
Reference:
Qi, H., Zhu, D., Wang, X., & Wu, J. (2024). Meta-analysis of the accuracy of the serum procalcitonin diagnostic test for osteomyelitis in children. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 25(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-024-07716-3
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


