- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Supra-patellar Approach Superior to Infra-patellar for Extra-articular Tibial Fractures-Study
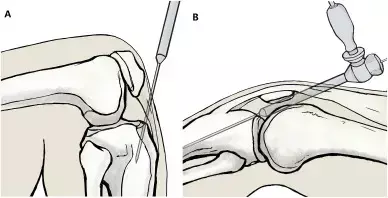
Intermedullary nailing (IMN) is the gold standard for the surgical treatment of extra-articular tibial fractures. The suprapatellar (SP) nailing approach offers several advantages over the conventional infrapatellar (IP) approach. However, most existing evidence is derived from retrospective observational studies.
Hu and Huang conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to compare the efficacy of the SP and IP approaches in extra-articular tibial fracture management. The article has been published in ‘BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.’
RCTs were searched in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, ClinicalTrials.gov, the Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar. Perioperative outcomes, visual analog scale (VAS) pain score, knee function metrics, and postoperative complications were compared using weighted mean difference (WMD) or risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). The certainty of evidence was evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach. All statistical analyses were performed using STATA 16.0 (StataCorp, TX, US).
The key findings of the study are:
• 13 RCTs encompassing 404 patients who underwent SP nailing and 396 who received IP nailing were included in the meta-analysis.
• RCTs were searched in PubMed, EMBASE, RCTs were searched in PubMed, EMBASE, SP approach was associated with significantly shorter operative time (WMD=-13.19 min, 95%CI: -24.37 to -2.02, p=0.021) and fluoroscopy time (WMD=-20.23, 95%CI:-39.74 to -0.71, p=0.042).
• The SP approach resulted in lower VAS pain score (WMD=-1.10, 95%CI: -1.90 to -0.31, p=0.007) and improved Lysholm knee score (WMD=4.22, 95%CI: 2.34 to 6.10, p<0.001) and KUJALA score (WMD=12.95, 95%CI: 10.78 to 15.13, p<0.001).
• No significant differences were observed in intraoperative blood loss, length of hospital stay, range of motion, union time, or complication rates (delayed union, nonunion, infection, secondary operation).
The authors concluded – “This meta-analysis of RCTs demonstrates that the SP approach offers several advantages over the IP approach, including shorter operative and fluoroscopy times, reduced postoperative pain, and improved knee function, with no increase in complication rates. These findings support the SP technique as a safe and effective alternative for the surgical treatment of extra-articular tibial fractures.”
Further reading:
Comparison of suprapatellar and infrapatellar intramedullary nailing for tibial fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Hu and Huang BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2025) 26:895 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-025-09162-1
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


