- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Use of quiet cast saw for cast removal lowers noise exposure compared to standard orthopaedic cast saws
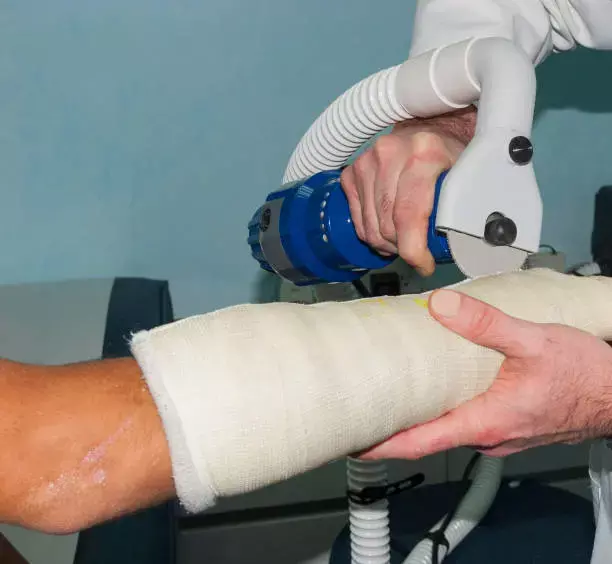
Cast removal can be associated with considerable noise exposure, especially impacting the pediatric patient and provider. Although noise generation from cast saws has been deemed safe by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention standards, there are no current studies on the effects of cast material on noise levels generated.
Aaron Shaw et al conducted the study at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dwight D. Eisenhower Army Medical Center, Fort Gordon, Georgia. It has been published in ‘the journal of bone & joint surgery.’
A simulated casting model utilizing plaster, fiberglass, and plaster with fiberglass overwrapping was used for experimental testing. Four different casting conditions were tested, with 5 samples in each group. Samples were tested using 2 different cast saws: a standard cast saw and a quiet saw. Each saw was used for 30 seconds of continuous cutting for each sample, measuring peak, mean, and minimum sound levels in decibels with sound level meters. Noise levels were measured at 18, 36, and 72 in (20, 91, and 183 cm) from the saw, comparing saw and cast types against ambient noise and baseline cast-saw noises. Between-group comparisons were performed using univariate analyses.
Key findings of the study were:
• Mean noise generation differed between casting materials, with plaster material demonstrating significantly greater noise levels than fiberglass casts at all distances for each saw type.
• Increasing fiberglass thickness significantly increased the mean noise levels with standard (18-in distance for 10 and 5 ply: 87.4 and 85.8 dB; p = 0.0004) and quiet cast saws (78.3 and 76.1 dB; p = 0.041).
• The quiet cast saw provided a 5.7 to 10.6 dB reduction in mean and peak noise levels, varying by casting material and distance.
The authors concluded that – “this study demonstrated that casting material and cast quality exhibit a significant influence on noise generation during cast removal. Fiberglass material produces significantly lower noise levels in comparison with plaster casting material during cast removal, and increasing cast thickness increases noise levels. These between-group differences, however, can be mitigated by incorporating quiet cast saws for removal, which also significantly reduce occupational noise exposure. As such, we recommend that providers pay close attention to casting material thickness during cast application to mitigate the risk of both unnecessary noise exposure and thermal injury. Although all casting groups did not exceed threshold noise exposure levels, we suggest the application of ALARA principles to noise exposure by consideration for either use of quiet cast saws during cast removal or the incorporation of patient and provider hearing protection to mitigate the occupational risk of noise-induced hearing loss.”
Further reading:
Understanding Noise Exposure During Cast Removal The Effect of Cast Saw Type and Casting Material
K. Aaron Shaw, Casey Mueller et al
TH E JOURNAL OF BONE & JOINT SURGERY- JBJS.ORG
VOLUME 104-A, NUMBER 17, S EPTEMBER 7, 2022
http://dx.doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.22.00158
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


