- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Well-controlled serum urate levels in gout linked to lower fracture risk
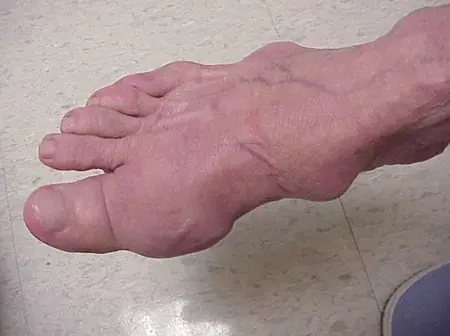
Well-controlled serum urate levels in gout result in lower fracture risk suggests a new study published in the Arthritis Rheumatology.
Gout is associated with a higher risk of fracture; however, the associations of hyperuricemia and urate-lowering therapy (ULT) with the risk of fracture have been inconsistent. We examined whether lowering serum urate (SU) levels with ULT to a target level (i.e., <360 μmol/L) reduces risk of fracture among people with gout.
Researchers emulated analyses of a hypothetical target trial using a “cloning, censoring, and weighting” approach to examine the association between lowering SU with ULT to the target levels and the risk of fracture using data from The Health Improvement Network, a United Kingdom primary care database. Individuals with gout who were 40 years or older and initiated ULT were included in the study.
Results
Among 28,554 people with gout, the 5-year risk of hip fracture was 0.5% for the “achieving the target SU level” arm and 0.8% for “not achieving the target SU level” arm, respectively. The risk difference and hazard ratio for “achieving the target SU level” arm was -0.3% and 0.66, respectively, compared with “not achieving the target SU level”. Similar results were observed when the associations of lowering SU level with ULT to the target levels with the risk of composite fracture, major osteoporotic fracture, vertebral fracture, and non-vertebral fracture were assessed.
In this population-based study, lowering the SU level with ULT to the guideline-based target level is associated with a lower risk of incident fracture in people with gout.
Reference:
Wei, J., Choi, H.K., Dalbeth, N., Lane, N.E., Wu, J., Lyu, H., Zeng, C., Lei, G. and Zhang, Y. (2023), Lowering serum urate with urate-lowering therapy to target and incident fracture among people with gout. Arthritis Rheumatol. Accepted Author Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.42504
Keywords:
Well-controlled, serum, urate levels, gout, result, lower, fracture risk, Arthritis Rheumatology, Wei, J., Choi, H.K., Dalbeth, N., Lane, N.E., Wu, J., Lyu, H., Zeng, C., Lei, G. and Zhang, Y.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


