Patients with Resistant Hypertension are at an Increased risk of3
Coronary Heart Disease
(HR:1.44 times)

Stroke
(HR:1.57 times)
All-Cause Mortality
(HR:1.30 times)
Heart Failure
(HR:1.88 times)
Pulmonary Artery Disease
(HR:1.23 times)
End-Stage Renal Disease
(HR:1.95 times)
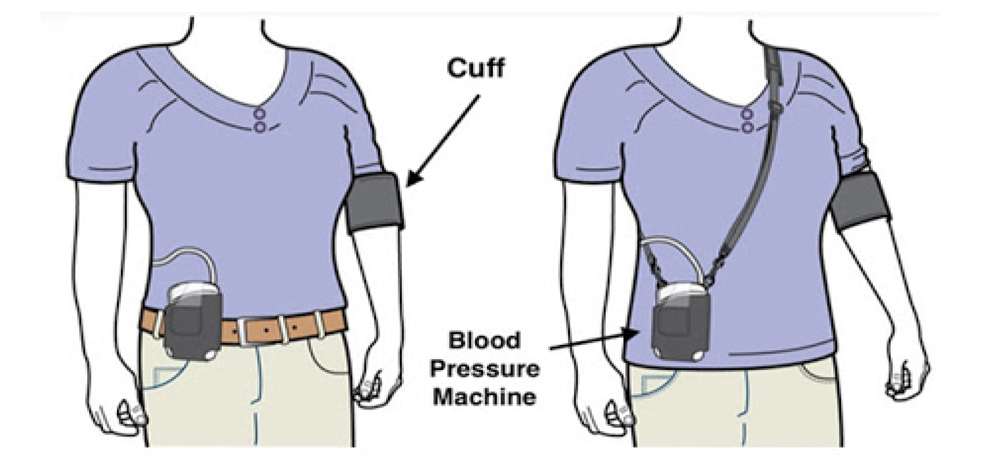
Ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM) Mandatory in Diagnosing Resistant Hypertension
American heart Association Defines:
Resistant hypertension (RH) is defined as above-goal elevated blood pressure (BP) in a patient despite the concurrent use of 3 antihypertensive drug classes, commonly including a long-acting calcium channel blocker, a blocker of the renin-angiotensin system (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker), and a diuretic.
The antihypertensive drugs should be administered at maximum or maximally tolerated daily doses.
RH also includes patients whose BP achieves target values on ≥4 antihypertensive medications.
 Old age (>55 years age) is the strongest5 predictor of Resistant Hypertension
Old age (>55 years age) is the strongest5 predictor of Resistant Hypertension
The Other6 predominant factors are:

Obesity

Diabetes

High baseline blood pressure
Leading factors7,9 that contribute to the development of Hypertension and Resistant Hypertension
Obesity

Physical inactivity

A diet high in
salt

Heavy alcohol intake
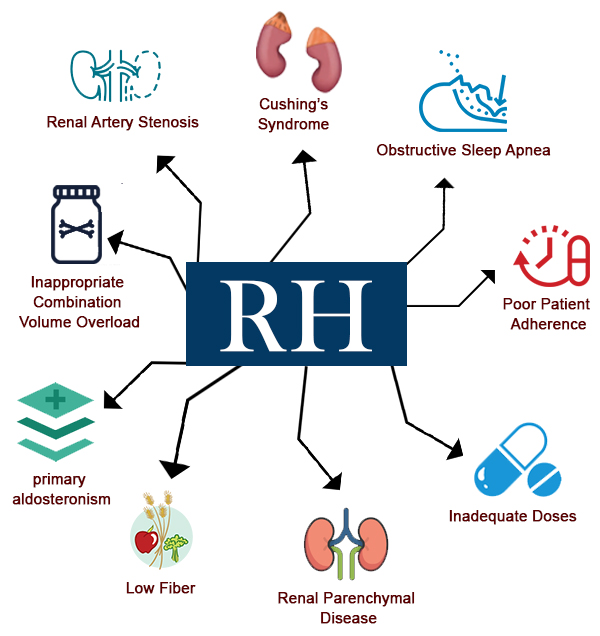
Secondary Causes10,11 of Resistant Hypertension
Therapy Guidelines
American Heart Association 2018 Guideline recommends 16
ARB + CCB + Diuretic (or loop diuretic)
As the first line treatment of resistant hypertension.
For GFR > 30 Ml/min - the diuretics with the greatest evidence base for reducing cardiovascular outcomes are the thiazide-like diuretics chlorthalidone. 18,19


For GFR < 30ml/min-A long-acting loop diuretic such as torsemide is favourable over shorter-acting agents such as bumetanide or furosemide. 17

AHA
Azilsartan is the choice of ARB

AHA
Long-acting Nifedipine superior to Amlodipine
ASN
Long-acting Nifedipine is the preferred choice of CCB in RHT2

AHA
Torsemide is the choice of diuretic for eGFR below 30 ml/min/1.73m2
The One Stop Solution…
In the Management of Tough to Control BP
Latest Posts
JOURNAL UPDATE
Contact us
for further information
References
1. Wolf-Maier et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA 289, 2363–2369 (2003).2. Daugherty SL et al. Incidence and prognosis of resistant hypertension in hypertensive patients. Circulation. 2012;125:1635–1642. 3. Muntner Petal.ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group: Treatment-resistant hypertension and the incidence of cardiovascular disease and end-stage renal disease: Results from the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Hypertension 64: 1012–1021, 2014pmid:25259745.4. Muntner Petal.ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group: Treatment-resistant hypertension and the incidence of cardiovascular disease and end-stage renal disease: Results from the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Hypertension 64: 1012–1021, 2014pmid:25259745.5. Lloyd-Jones DM, Evans JC, Larson MG, O'Donnell CJ, Rocella EJ, Levy D. Differential control of systolic and diastolic blood pressure: factors associated with lack of blood pressure control in the community. Hypertension. 2000; 36: 594–599.6. Cushman WC, Ford CE, Cutler JA, Margolis KL, Davis BR, Grimm RH, Black HR, Hamilton BP, Holland J, Nwachuku C, Papademetriou V, Probstfield J, Wright JT, Alderman MH, Weiss RJ, Piller L, Bettencourt J, Walsh SM, for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Success and predictors of blood pressure control in diverse North American settings: the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering and Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). J Clin Hypertens. 2002; 4: 393–404. Crossref.7. Nishizaka MK et al. Validity of plasma aldosterone-to-renin activity ratio in African American and white subjects with resistant hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:805–812.8. He FJ et al. Effect of longer-term modest salt reduction onblood pressure. The Cochrane Database of Systemic Reviews. 2004;(3): 9. Henningsen NC et al. Hypertension, levels of serum gamma glutamyl transpeptidase and degree of blood pressure control in middle-aged males. Acta Med Scand.1980;207:245–251. 10. J. P. Garg et al. Resistant hypertension revisited: a comparison of two university-based cohorts; American Journal of Hypertension, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 619–626, 2005. 11. Chobanian AV et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003, 289:2560-2572. 10.1001/jama.289.19.2560. 12. Whelton PK et al.: 2017ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary:a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2018, 138:426-483. 13. Chapman N et al.Effect of spironolactone on blood pressure in subjects with resistant hypertension. Hypertension. 2007,49:839-845. 14. Pickering TG et al.Recommendations of blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals. Part 1:blood pressure measurement in humans. A Statement for Professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. 15. Egan BM et al.Blood pressure control provides less cardiovascular protection in adults with than without apparent treatment-resistant hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016;18:817–824. 16. Hypertension. 2018 Nov;72(5):e53-e90. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000084.