- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Eye ultrasounds may assist with detecting brain shunt failure in children: Study
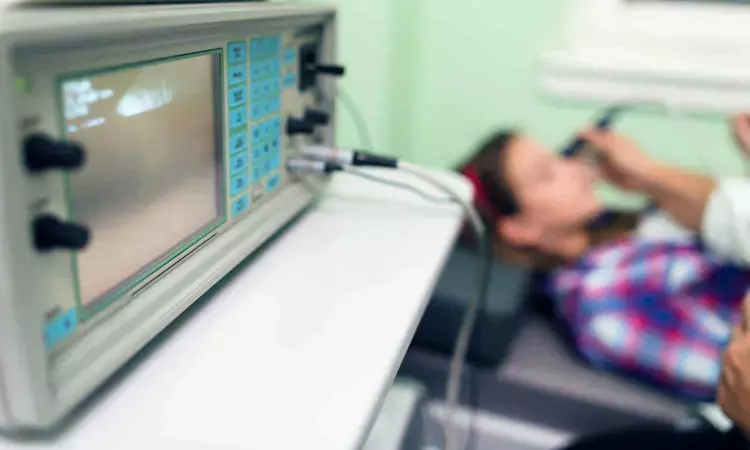
Use of an eye ultrasound may quickly and safely identify children with brain drainage tube failure in the emergency department, according to a new study. The research will be presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2024 Meeting, held May 3-6 in Toronto.
A ventricular shunt is a surgically implanted thin, plastic tube that drains extra fluid and relieves pressure on the brain. Children receive ventricular shunts for hydrocephalus, a condition where brain fluid doesn’t drain or reabsorb properly from brain bleeds, tumors, or other causes. Nearly 30% of shunts break, are displaced, or become blocked within two years of placement, and another 5% fail each year after that, experts say.
When a patient visits the emergency department for potential shunt failure, their symptoms are often nonspecific, including headache, vomiting, and fatigue, according to researchers. Shunt failure is life threatening, and children with shunts typically undergo multiple computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans per year, exposing them to excessive radiation and sedation. A backup of fluid causes the optic nerve sheath to swell, which researchers can measure with eye ultrasound.
The study found that comparing the diameter of the optic nerve when a patient is symptomatic to the diameter when they are well can help determine if a shunt is blocked.
“The research team is interested in finding ways to lessen radiation exposure and expedite diagnosing shunt failure in the emergency department,” said Adrienne L. Davis, MD, MSc, FRCPC, pediatric emergency medicine research director at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) and presenting author. “The study uses patients as their own controls by measuring the optic nerve when well and sick—a strategy that individualizes this test for every patient and recognizes that every patient with a shunt has a unique degree of shunt dependence and ability to tolerate high brain pressures.”
The researchers studied 76 pairs of eye ultrasounds of nearly 60 children presenting to the Toronto hospital’s emergency department with potential shunt failure. Researchers note that while findings are promising, results require further confirmation in a larger population of children with shunts across North America.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


