- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Isolated diastolic hypertension in childhood increases risk of adult subclinical target organ damage
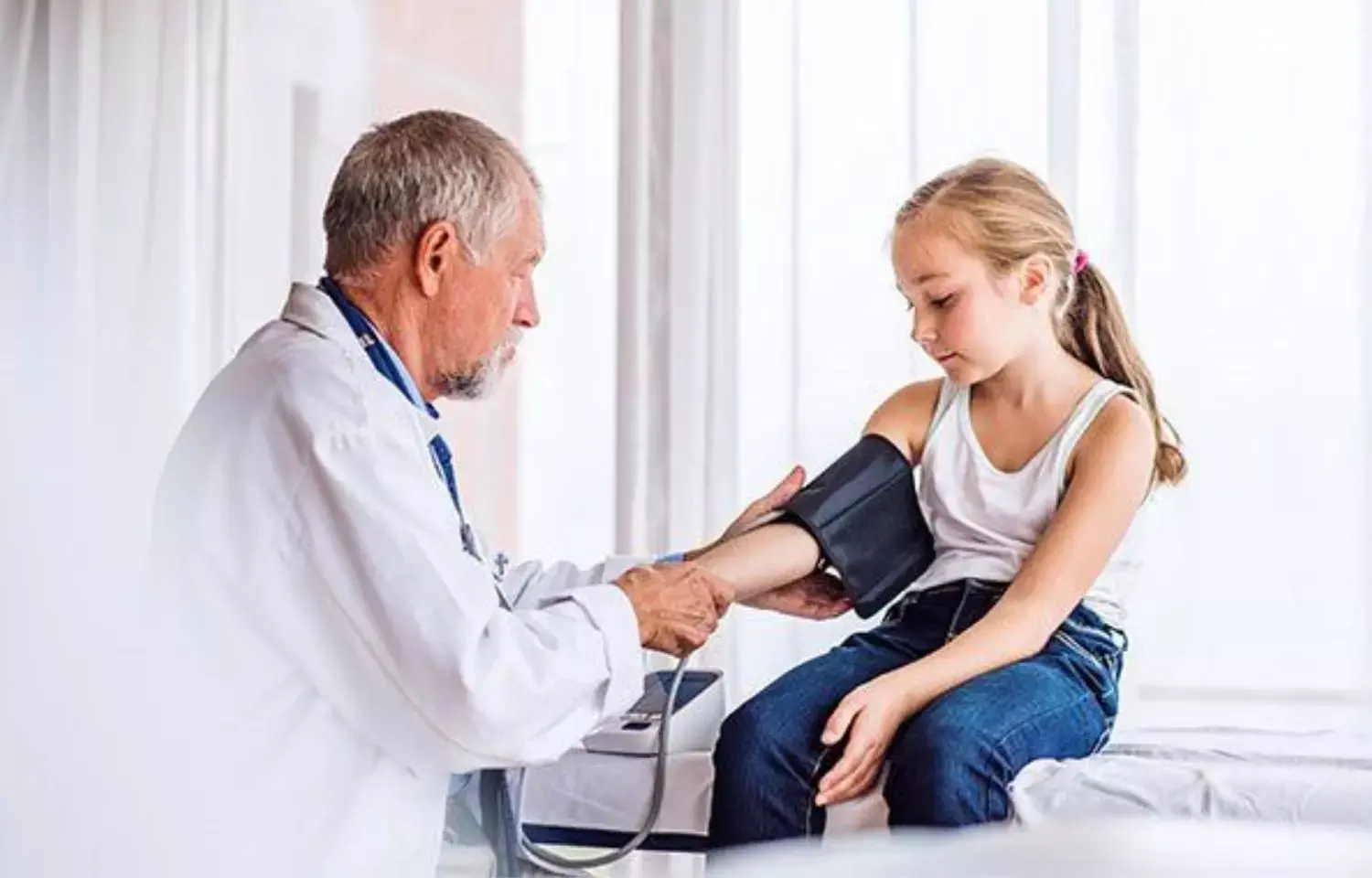
China: Isolated diastolic hypertension (IDH) accounts for a higher proportion of adolescent hypertension subtypes and can increase the risk of adult subclinical target organ damage (STOD), showed a 30-year prospective cohort study results published in the Journal of Hypertension.
Hypertension is one of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Hypertension guidelines subdivide hypertension into IDH, ISH, and mixed hypertension. Isolated diastolic hypertension (IDH) is a largely unrecognized subtype of hypertension, more commonly seen in the younger age group. IDH has usually been neglected and the treatment and awareness rates of this condition remain low. Previous studies have shown that the relationship between IDH and cardiovascular outcomes is strongly associated with age but they have focused on adults or the elderly. Data on the association of IDH in childhood with adult cardiovascular risk are scarce.
Liao, Xi'an Jiaotong University, China, and colleagues conducted a study to estimate the prevalence of IDH in adolescents and to explore the impact of IDH in childhood on adult subclinical target organ damage.
Fo the longitudinal study, researchers enrolled 1738 school children (55.4% boys) aged 6–15 years and followed them for 30 years. Their blood pressure was recorded to define the hypertension subtypes: normotension, IDH, isolated systolic hypertension (ISH), and mixed hypertension. Tracked STOD included arterial stiffness (n = 1738), albuminuria (n = 1652) and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) (n = 1429).
Key findings of the study,
• The prevalence of IDH, ISH and mixed hypertension was 5.4%, 2.2%, and 3%, respectively, and there was no gender difference.
• Over 30 years, 21.1% of participants developed arterial stiffness, 10.3% developed albuminuria, and 4.8% developed LVH.
• Compared with normotensive participants, IDH in childhood had a higher risk ratio (RR) of experiencing arterial stiffness (RR-1.66) and albuminuria (RR-2.27) in adults after being fully adjusted but not LVH.
• If the elevated BPin children were to be used as the reference standard, IDH in childhood was associated with adult LVH (RR-2.48).
The authors conclude that IDH accounts for a higher proportion of adolescent hypertension subtypes. The key finding was that IDH in childhood significantly increased the risk of some measures of subclinical target organ damage in adults. The cumulative long-term burden and longitudinal trends of Diastolic BP from childhood to adulthood were also associated with target organ measurements in adults.
The study results emphasize the requirement of improving the prevention, detection, and treatment of isolated diastolic hypertension in adolescents, the authors commented.
Reference:
Liao Y, Chu C, Wang Y, Zheng W, Ma Q, Hu J, Yan Y, Yang J, Yang R, Wang K, Yuan Y, Chen C, Sun Y, Mu J. Isolated diastolic hypertension in childhood and risk of adult subclinical target organ damage: a 30-year prospective cohort study. J Hypertens. 2022 Jun 22. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003183. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35730419.
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


