- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Nebulized Poractant alfa and nCPAP combo fails to reduce respiratory failure in preemies: Study
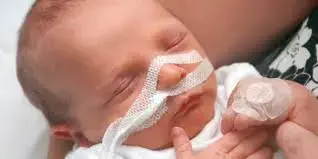
Nebulized Poractant alfa (at 200 and 400 mg/kg doses) delivered in combination with nasal continuous positive airway pressure (nCPAP) not effective in treating respiratory distress syndrome in premature babies, according to a new study published in the The Journal of Pediatrics
A study was conducted to investigate the efficacy and safety of nebulized Poractant alfa (at 200 and 400 mg/kg doses) delivered in combination with nasal continuous positive airway pressure (nCPAP) compared with nCPAP alone in premature babies with diagnosed RDS.
This randomized, controlled, multinational study was conducted in 28+0 to 32+6 weeks gestation infants. The primary outcome was the incidence of respiratory failure in the first 72 hours of life, defined as needing endotracheal surfactant and/or mechanical ventilation due to prespecified criteria. Secondary outcomes included the time to respiratory failure in the first 72 hours, duration of ventilation, mortality, incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and major associated neonatal comorbidities. In addition, the safety and tolerability of the treatments were assessed reporting the number and percentage of babies with treatment-emergent adverse events and adverse drug reactions during nebulization.
Results
129 babies were randomized. No significant differences were observed for the primary outcome: 24 (57%), 20 (49%) and 25 (58%) infants received endotracheal surfactant and/or mechanical ventilation within 72 hours in the Poractant alfa 200 mg/kg, Poractant alfa 400 mg/kg and nCPAP groups, respectively. Similarly, secondary respiratory outcomes did not differ among groups. Enrollment was halted early due to a change in the benefit-risk balance of the intervention. Nebulized Poractant alfa was well tolerated and safe, and no serious adverse events were related to the study treatment.
Thus, nebulized poractant alfa (at 200 and 400 mg/kg doses) delivered in combination with nasal continuous positive airway pressure did not reduce the likelihood of respiratory failure within the first 72 hours of life.
Reference:
A Randomized, Controlled Trial to Investigate the Efficacy of Nebulized Poractant Alfa in Premature Babies with Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Carlo Dani, et al. published in The Journal of Pediatrics.
https://www.jpeds.com/article/S0022-3476(22)00175-5/fulltext
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


