- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Endobronchial OCT safe and accurate method for microscopic ILD diagnosis: Study
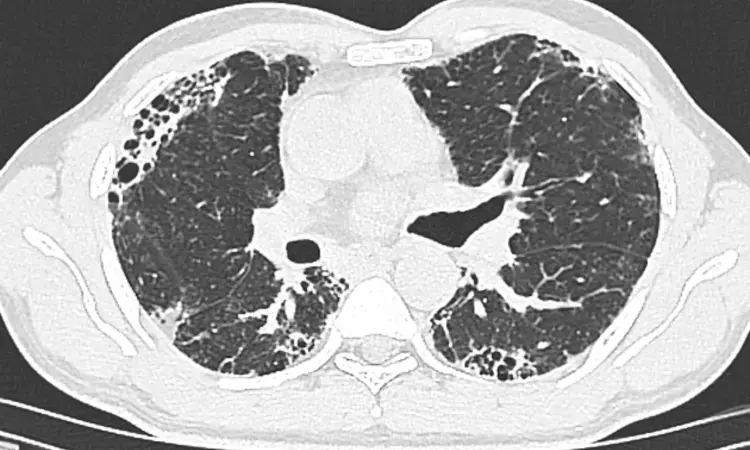
Endobronchial Optical Coherence Tomography is a highly safe and effective technique for microscopic diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD), suggests a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
Early, accurate diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD) informs prognosis and therapy, especially in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Current diagnostic methods are imperfect. HRCT resolution is limited while surgical lung biopsy (SLB) carries risks of morbidity/mortality. Endobronchial optical coherence tomography (EB-OCT) is a low-risk, bronchoscope-compatible modality that images large lung volumes in vivo with microscopic resolution, including subpleural lung, and has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of bronchoscopy for ILD diagnosis. Objectives:
A group of researchers U.S.A performed a prospective diagnostic accuracy study of EB-OCT in ILD patients with a low-confidence diagnosis undergoing SLB.
Primary endpoints were EB-OCT sensitivity/specificity for the diagnosis of the histopathologic pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) and clinical IPF. The secondary endpoint was an agreement between EB-OCT and SLB for diagnosis of the ILD fibrosis pattern. Methods: EB-OCT was performed immediately prior to SLB.
The resulting EB-OCT images and histopathology were interpreted independently by blinded, independent pathologists. Clinical diagnosis was obtained from the treating pulmonologists after SLB, blinded to EB-OCT.
The researchers enrolled 31 patients and four were excluded due to inconclusive histopathology or lack of EB-OCT data. Twenty-seven patients were included in the analysis of which, twelve were diagnosed with UIP and fifteen with non-UIP ILD.
The results of the study are as follows:
Average forced vital capacity and DLCO were 75.3% and 53.5% respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of EB-OCT was 100% and 100% respectively, for both histopathologic UIP and clinical diagnosis of IPF.
There was high agreement between EB-OCT and histopathology for diagnosis of ILD fibrosis pattern.
Thus, the researchers concluded that EB-OCT is a safe, accurate method for microscopic ILD diagnosis, as a complement to HRCT and alternative to SLB.
Reference:
Diagnostic Accuracy of Endobronchial Optical Coherence Tomography for the Microscopic Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia by Nandy S et. al published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202104-0847OC
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


