- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Sputum Eosinophils Complementary Tools for Diagnosing Occupational Asthma: Study
Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Sputum Eosinophils are Complementary Tools for Diagnosing Occupational Asthma suggests a study published in the Allergy.
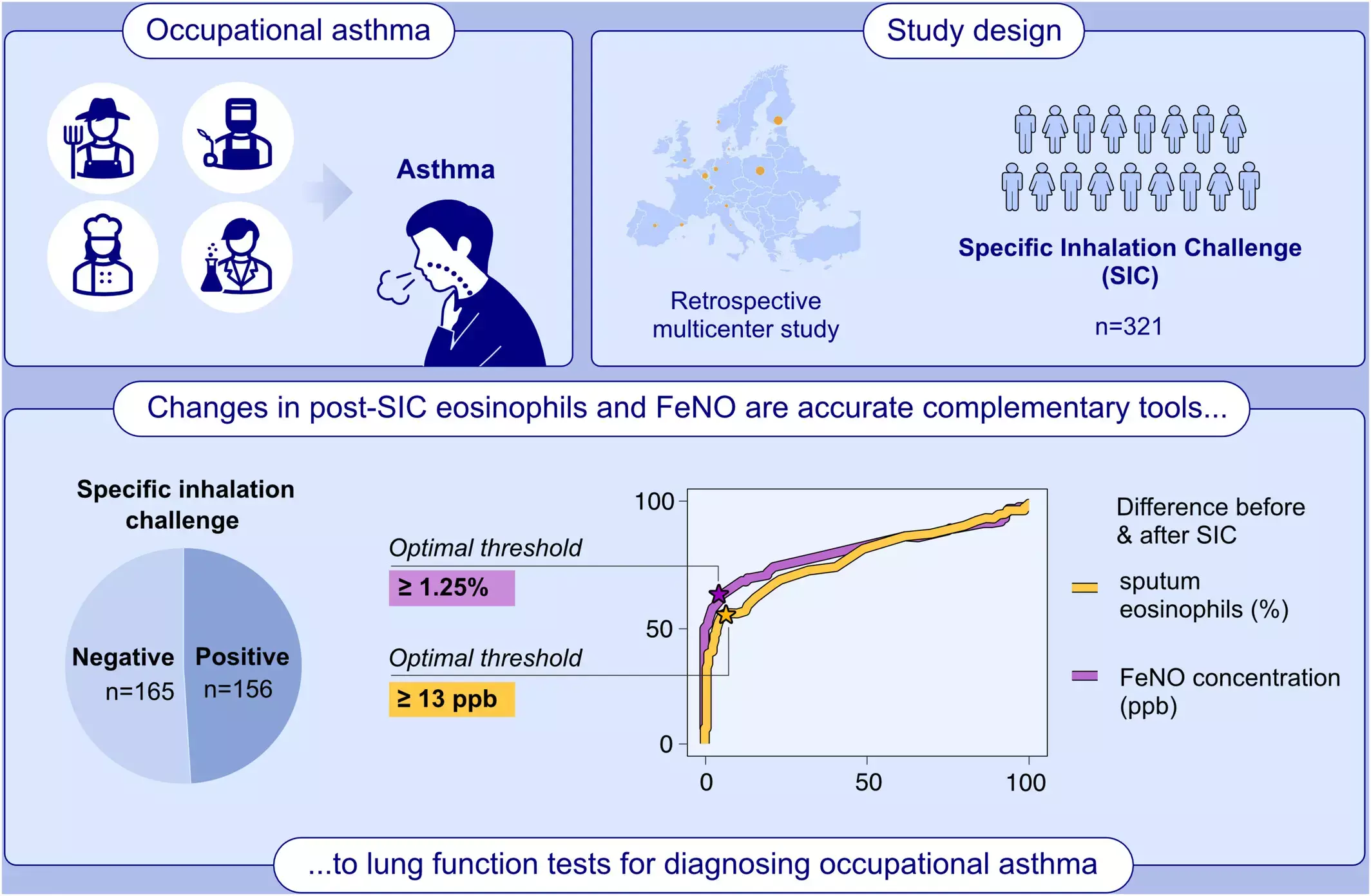
Exposure-related changes in exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and sputum eosinophils have not been thoroughly compared in the investigation of occupational asthma. This study aimed to compare the accuracies of the changes in FeNO concentrations and sputum eosinophil counts in identifying asthmatic reactions induced by occupational agents during specific inhalation challenges (SICs).
This retrospective multicenter study included 321 subjects who completed an assessment of FeNO and sputum eosinophils before and 24 hours after SICs with various occupational agents, of whom 156 showed a positive result. Results: Post-challenge changes in FeNO and sputum eosinophils showed similar accuracies, with areas under the receiver operating characteristics curve of 0.78 (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.72-0.83) and 0.81 (95% CI, 0.76-0.86), respectively. Increases in FeNO level ≥ 13 ppb and sputum eosinophils ≥ 1.25% were identified as the optimal threshold values for differentiating positive from negative SICs.
Using these thresholds, the changes in FeNO and sputum eosinophils each achieved a ≥ 95% specificity but a low sensitivity (55% and 62%, respectively). FeNO and sputum eosinophils showed discordant increases in 38% of subjects with a positive SIC. Combining either a rise in FeNO ≥ 13 ppb or an increase in sputum eosinophils ≥ 1.25% increased the sensitivity to 77%. Increases in FeNO concentration and/or sputum eosinophils after exposure to occupational agents strongly support a diagnosis of occupational asthma. The assessment of both markers of airway inflammation should be regarded as a reliable complementary tool to spirometry for identifying bronchial responses to occupational agents.
Reference:
Doyen V, Migueres N, van Kampen V, Suojalehto H, Mason P, Munoz X, Sastre J, Quirce S, Svanes C, Walters G, Moore V, Jacobsen IB, Folletti I, Preiser AM, Walusiak-Skorupa J, Rifflart C, de Blay F, Vandenplas O; European network for the PHenotyping of OCcupational ASthma (E‐PHOCAS). Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Sputum Eosinophils Are Complementary Tools for Diagnosing Occupational Asthma. Allergy. 2024 Dec 27. doi: 10.1111/all.16447. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39726396.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


