- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Incidence of PE nine fold higher in patients with Covid-19, finds study
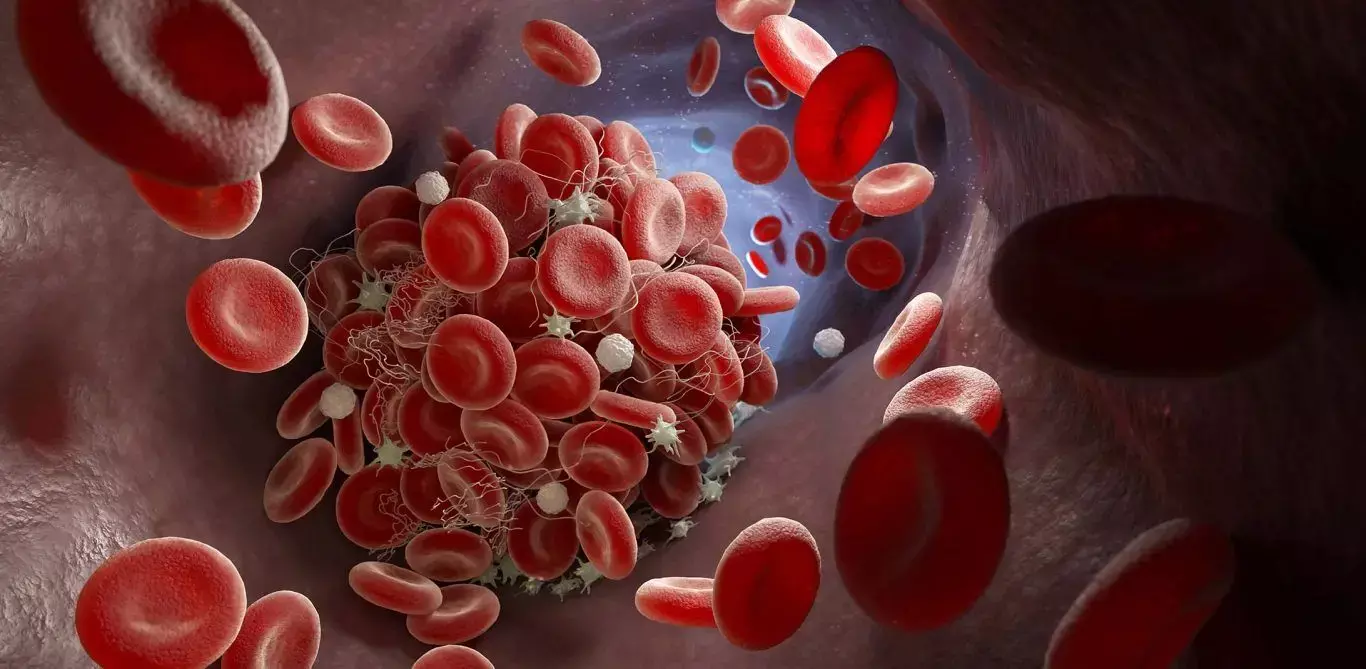
Infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 promotes a pro-coagulant state, detected by increased D-dimer levels and is related to complications.
Oscar Miro et.al, designed a study by including patients attending emergency department (ED) with pulmonary embolism (PE) at 62 ED's in Spain with following objectives
1) to determine the relative frequency of PE in patients with COVID-19 coming to the ED and estimate the standardized incidence in the general population
2) to uncover the risk factors associated with the development of PE in patients with COVID-19
3) to describe whether there is any distinctive clinical characteristic in these patients in comparison with PE observed in non-COVID-19 patients
4) to investigate the outcome of COVID-19 patients presenting with PE
COVID-19 patients without PE and non-COVID-19 patients with PE were included as control groups.
A total of 368 patients with PE were included and analyzed.
Following observations were noted from the study.
1) The standardized incidence of PE in the COVID-19 population resulted in 310 per 100 000 person-years, significantly higher than that observed in the non- COVID-19 population which is 35 per 100 000 person-years.
2) Several characteristics in COVID-19 patients were independently associated with PE, the strongest being D-dimer >1000 ng/mL, and chest pain.
3) COVID-19 patients with PE differed from non-COVID-19 patients with PE in 16 characteristics, most directly related to COVID-19 infection; remarkably, D-dimer >1000 ng/mL, leg swelling/pain, and PE risk factors were significantly less present.
4) PE in COVID-19 patients affected smaller pulmonary arteries than in non-COVID-19 patients, although right ventricular dysfunction was similar in both groups.
5) In-hospital mortality in cases was similar to COVID-19 patients without PE, but higher than in non-COVID-19 patients with PE.
Authors concluded that incidence of PE is nine fold higher in patients with Covid-19 as compared to non Covid-19 population and presence of above characteristics should warrant for initiation of anticoagulation.
Source: European Heart Journal
MBBS, M. D. Respiratory Medicine
Dr Sravan Kumar V, completed his M. B. B. S from SRMC, Nandyal and M. D. in Respiratory Medicine from the JSS Medical College, Mysore. After completing MD. he worked as Senior resident in Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. He is actively involved in various research activities of the department. Currently he is working as senior resident in Mallareddy medical college for women, Hyderabad. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


