- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Untreated sleep apnea patients more likely to be hospitalized for flu Infection
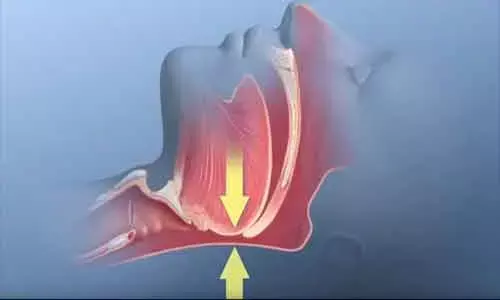
DARIEN, IL -OBJECTIVES:There is evidence that sleep deprivation or diseases such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) that lead to sleep disruption may adversely impact immune system functioning.
A study published online as an accepted paper in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine is the first to find that patients with sleep apnea who did not use CPAP therapy were more likely to be hospitalized with the flu. Adults with obstructive sleep apnea may need to take extra precautions in flu season.
Results of the retrospective study show that 61% of patients (17 of 28) who either weren't prescribed CPAP to treat their sleep apnea or weren't adherent to their CPAP treatment were hospitalized with the flu, compared with 24% of patients (6 of 25) who were adherent to CPAP therapy. Statistical analysis found that the patients who were non-adherent to CPAP were nearly five times more likely to be hospitalized with a flu infection, despite having a higher rate of flu vaccination.
"Our study would suggest that among patients with obstructive sleep apnea, those who use CPAP are less likely to be hospitalized because of an influenza infection than those who do not use CPAP," said study coinvestigator Dr. Glen Greenough, associate professor of medicine, psychiatry and neurology at the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center in Lebanon, New Hampshire.
Greenough said the study provides further evidence that sleep is essential to health.
"These results would suggest that use of a treatment, CPAP, that improves sleep quality reduces the severity of influenza infection as determined by rate of hospitalization," he said. "This might suggest that treating sleep apnea and thereby improving sleep quality has a beneficial effect on the immune system. It also suggests that treating sleep apnea with CPAP could help reduce hospitalizations thereby reducing health care costs."
Nearly 30 million adults in the U.S. have obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic disease that involves the repeated collapse of the upper airway during sleep. Common warning signs include snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness. A common treatment is CPAP therapy, which uses mild levels of air pressure, provided through a mask, to keep the throat open during sleep.
The researchers at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center analyzed the medical records of 53 patients who had sleep apnea and a confirmed case of the flu between 2016-2018. The 28 patients categorized as non-adherent to CPAP treatment had a mean age of 63 years and were 54% male; the 25 CPAP-adherent patients had a mean age of about 60 years and were 52% male. CPAP use was assessed by data download, with adherence defined as usage of at least four hours per night for at least 70% of nights.
The analysis also revealed that 75% of non-adherent patients received a flu vaccine, compared with 56% of regular CPAP users. While not a statistically significant difference, the authors suggest that poor sleep could have negatively impacted non-adherent patients' response to the vaccine.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, October is a good time to get vaccinated for the flu. Learn more at cdc.gov/flu.
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


