- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Can PET help diagnose neurosarcoidosis?
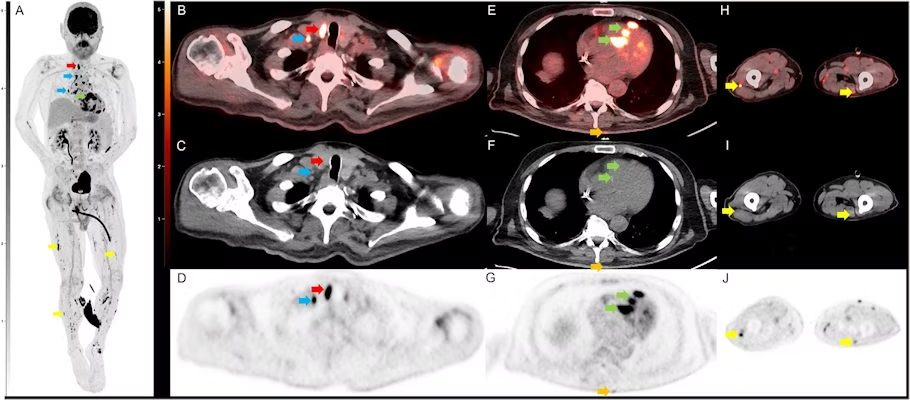
FDG-PET imaging shows promise for use as a diagnostic criterion for neurosarcoidosis, with a recent case series illustrating the approach was effective when gold-standard approaches were not, according to a group of researchers in Berlin.
The diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis (NS) remains challenging due to the difficulty to obtain central nervous system (CNS) biopsies. Various diagnostic parameters are considered for the definition of possible, probable and definite NS. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the imaging gold standard and considered in diagnostic criteria. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission (18F-FDG PET) is sometimes performed additionally to identify possible systemic biopsy targets. However, at present, its findings are not incorporated into the diagnostic criteria for neurosarcoidosis (NS). They conducted a single center retrospective search for the period 2020–2022, for patients with neurological symptoms in a diagnostic context of suspected NS who underwent MRI and additional 18F-FDG PET scans to identify potential hypermetabolism in the CNS and biopsy targets.Results: They identified three cases of NS, where Gadolinium-enhanced MRI scans did not show abnormalities while 18F-FDG PET revealed hypermetabolic lesions in areas of the CNS. Additional MRI scans were still inconclusive for structural changes. We diagnosed a “probable” NS in all cases with histopathological confirmation of systemic sarcoidosis which led to an intensified therapy regime. 18F-FDG PET is an early indicator for metabolic changes. It appears to be a useful add-on to improve accuracy of diagnostic criteria in suspected NS without MRI findings.
Reference:
Chen, J., Metzger, G., Furth, C. et al. Reevaluating the relevance of 18F-FDG PET findings for diagnosis of neurosarcoidosis: a case series. Neurol. Res. Pract. 6, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-023-00299-9
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


