- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
CT-guided renal ablation safe alternative to nephrectomy for cancer treatment in obese: Study
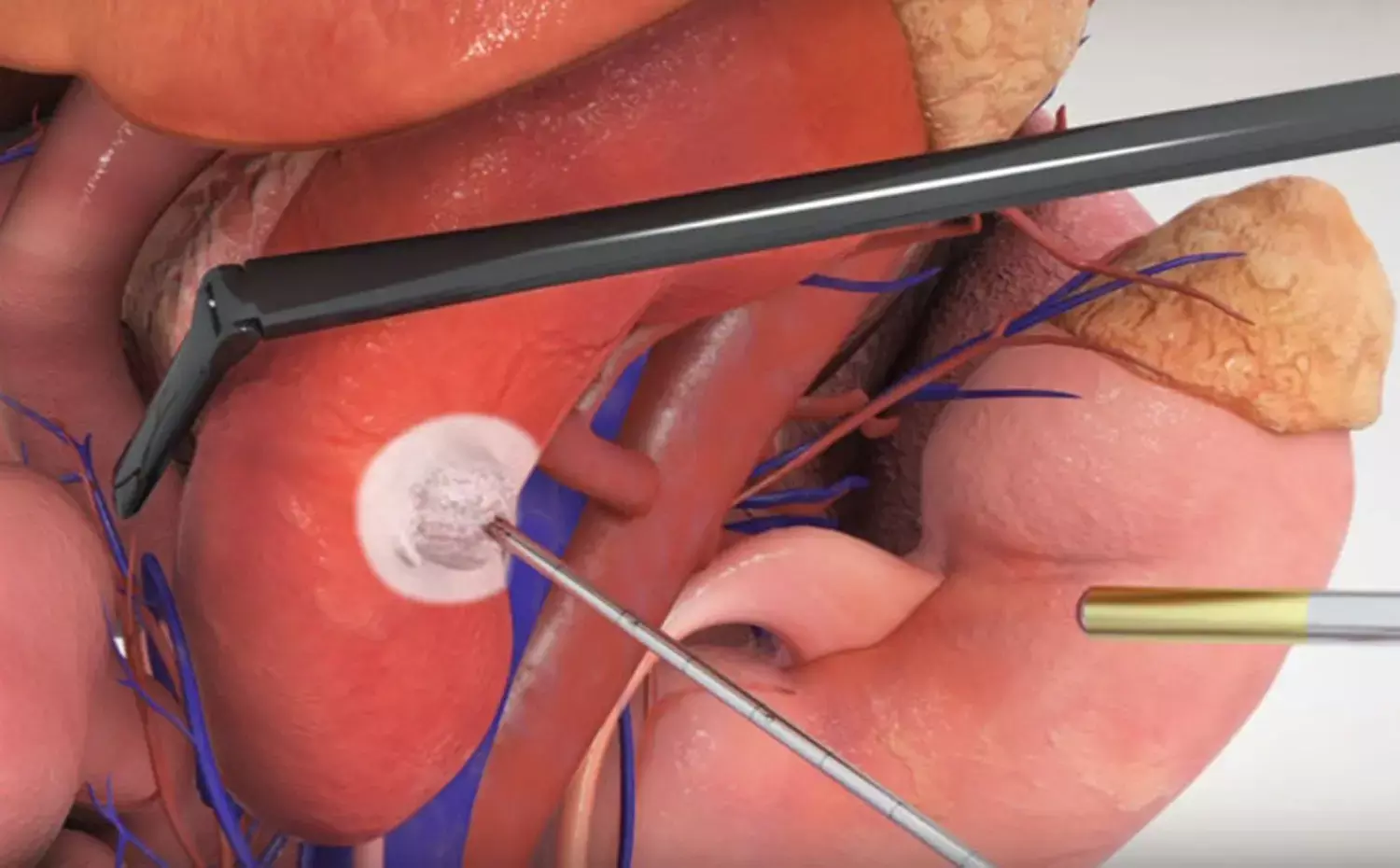
USA: CT-guided thermal ablation is a safe and effective treatment for renal cell carcinoma in morbidly obese patients and can be considered as an alternative to nephrectomy, suggests a recent study American Journal of Roentgenology.
Obesity is a global problem that impacts patient health and morbidity associated with surgical procedures. Thus, morbid obesity patients may not be suitable candidates for curative surgery. Wenhui Zhou, Department of Radiology, Stanford Medicine, Stanford, CA, and colleagues aimed to determine the feasibility, oncologic outcomes, and survival of patients with morbid obesity and renal cell carcinoma treated with thermal ablation.
For the purpose, the researchers performed a retrospective analysis of 107 patients treated with CT-guided renal ablation for clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma between February 2005 and December 2017.
Patients were stratified into two cohorts on body mass index of ≥ 40 kg/m2 (morbidly obese) and body mass index of 18.5–24.9 kg/m2 (normal weight). Anesthetic and radiation dosages, procedure time, residual disease, and local recurrence, and adverse events were analyzed between the two groups.
Key findings of the study include:
- Thirty-four patients were morbidly obese, and 73 patients had normal weight.
- Morbid obesity was associated with longer procedural duration, sedative doses and radiation exposure than normal weight.
- Hematomas were more prevalent in patients with morbid obesity than in those of normal weight, but treatment efficacy and local recurrences were comparable with those for normal-weight individuals.
- Cancer-related outcomes were equivalent between the two groups based on 5 years of imaging observation data.
"CT-guided thermal ablation remains technically feasible, well-tolerated, and effective in patients with morbid obesity and renal cell carcinoma, with the caveat of increased risk of perinephric hematoma, anesthesia dose, and radiation exposure," wrote the authors.
The study titled, "Thermal Ablation of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Patients With Morbid Obesity: Assessment of Technique, Safety, and Oncologic Outcomes," is published in the American Journal of Roentgenology.
DOI: https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.20.23803
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


