- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Echocardiographic features of cardiac masses can accurately diagnose malignancy
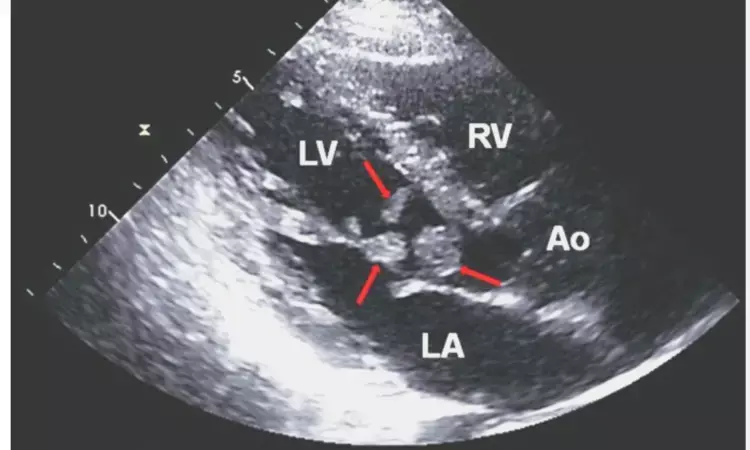
Italy: A recent study has shown that some echocardiographic parameters of cardiac masses (CMs) can serve as markers for the accurate prediction of malignancy, informing the call for second-level investigations and minimizing delays in diagnosis in such a complex clinical scenario. The study's findings appeared in the Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography.
There is no information on the echocardiographic parameters needed for a comprehensive assessment of cardiac masses. Therefore, Pasquale Paolisso from the University of Naples in Federico II, Naples, Italy, and colleagues aimed to identify and integrate the CM's echocardiographic features that can accurately predict malignancy.
For this purpose, the team conducted an observational cohort study of 286 successive patients who underwent a standard echocardiographic examination for suspected cardiac mass in Bologna University Hospital between 2004 and 2022. Histological analysis was used to achieve a definitive diagnosis, or, in the case of cardiac thrombi, with radiological evidence of thrombus resolution after appropriate anticoagulant treatment.
To confirm the ability of six echocardiographic parameters to discriminate malignant from benign masses, logistic and multivariable regression analysis was performed. The unweighted count of these parameters was utilized as a numerical score, varying from 0 to 6, with a cut-off of more than three, balancing specificity and sensitivity concerning the histological diagnosis of malignancy. Classification tree analysis was used to find the ability of echocardiographic parameters to distinguish sub-groups of patients with a differential risk of malignancy.
The study led to the following findings:
· Benign masses were more frequently mobile, pedunculated, and adherent to the interatrial septum.
· Malignant masses demonstrated a greater diameter and exhibited a higher irregular margins frequency, an inhomogeneous appearance, polylobate shape, sessile implantation, and pericardial effusion.
· In both univariate and multivariable models, infiltration, non-left localization, moderate-severe pericardial effusion, polylobate, sessile, and inhomogeneity were confirmed to be independent malignancy predictors.
· The predictive ability of the unweighted count of >3 was very high (>0.90) and similar to that of the previously published weighted score.
· The CTA produced an algorithm in which infiltration was the best distinguisher of malignancy, followed by non-left localization and sessile shape.
· The percentage correctly distinguished by the CTA as malignant was 87.5%.
· The range of agreement between observer readings and cardiac mass histology was between 85.1-91.5%.
· At least three echocardiographic parameters were associated with lower survival.
To conclude, an algorithm was generated that correctly classified 87.5% of the malignancies. These echocardiographic features proved to have also prognostic validity.
Reference:
Paolisso, P., Foà, A., Bergamaschi, L., Graziosi, M., Rinaldi, A., Magnani, I., Angeli, F., Stefanizzi, A., Armillotta, M., Sansonetti, A., Fabrizio, M., Amicone, S., Impellizzeri, A., Tattilo, F. P., Suma, N., Bodega, F., Canton, L., Gherbesi, E., Tuttolomondo, D., . . . Pizzi, C. (2023). Echocardiographic Markers in the Diagnosis of Cardiac Masses. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2022.12.022
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


