- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
FAPI-PET better than standard molecular imaging for diagnosis of gastric cancer, study finds
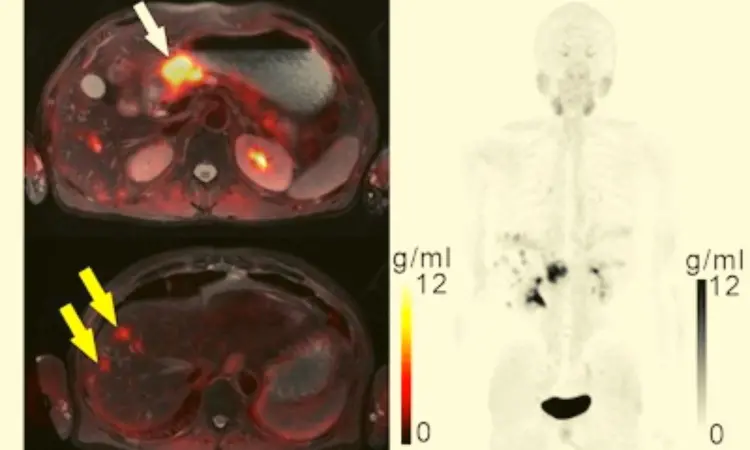
China: A recent study publshed in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine, reveals that 68Ga-FAPI PET/MR outperforms 18F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosing gastric cancer.
"Hybrid PET/MR imaging with an experimental gallium-68 (Ga-68)-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) radiotracer perforend better than standard molecular imaging in visualizing the primary and most metastatic lesions of gastric cancer and could be a promising method," Chunxia Qin, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues wrote in their study.
Gastric cancer is the fifth most common malignant tumor and their common cause of cancer death worldwide. Its characteristics include high incidence, high mortality rate, high metastasis rate, low radical resection rate, low early diagnosis rate, and low 5-y survival rate. Many gastric cancer patients present with advanced-stage disease because of the lack of specific early signs and symptoms. Thereby early diagnosis and accurate staging are essential for choosing an appropriate therapy strategy.
18F-FDG PET/CT is used extensively in the diagnosis, staging, and preoperative evaluation of gastric cancer. However, it is associated with a low detection rate for primary gastric cancer (∼55%), especially in the early stage, as well as signet-ring cell, mucinous, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas, which are typically less metabolically active.
Against the above background, the authors aimed to evaluate the performance of 68Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 (68Ga-FAPI) PET/MR for the diagnosis of primary tumor and metastatic lesions in patients with gastric carcinomas and to compare the results with those of 18F-FDG PET/CT.
For this purpose, the researchers recruited twenty patients with histologically proven gastric carcinoma. Each patient underwent both 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI PET/MR. To compare the detectability of primary tumors and metastases in different organs or regions, a visual scoring system was established.
They measured the original SUVmax and normalized SUVmax of selected lesions on both 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI PET/MR. Normalized SUVmax was calculated by dividing a lesion's original SUVmax with the SUVmean of the descending aorta. Original/normalized SUVmax-FAPI and SUVmax-FDG were compared for patient-based (including a single lesion with the highest activity uptake in each organ/region) and lesion-based (including all lesions [≤5] or the 5 lesions with highest activity [>5]) analyses, respectively.
The study recruited 20 patients (median age: 56.0 y; range: 29–70 y) including 9 men and 11 women, 14 patients for initial staging and 6 for recurrence detection.
Following were the study's key findings:
- 68Ga-FAPI PET was superior to 18F-FDG PET for primary tumor detection (100.00% [14/14] vs. 71.43% [10/14]), and the former had higher tracer uptake levels.
- 68Ga-FAPI PET was superior to 18F-FDG PET in both patient-based and lesion-based evaluation except for the metastatic lesions in supradiaphragmatic lymph nodes and ovaries.
- Multiple sequences of MR images were beneficial for the interpretation of hepatic metastases in 3 patients, uterine and rectal metastases in 1 patient, ovarian lesions in 7 patients, and osseous metastases in 2 patients
To conclude, 68Ga-FAPI PET/MR outperformed 18F-FDG PET/CT in visualizing primary and metastatic lesions of gastric cancer and may potentially replace 18F-FDG PET/CT.
Reference:
8Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/MR in the Evaluation of Gastric Carcinomas: Comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT Chunxia Qin, Fuqiang Shao, Yongkang Gai, Qingyao Liu, Weiwei Ruan, Fang Liu, Fan Hu, Xiaoli Lan Journal of Nuclear Medicine Jan 2022, 63 (1) 81-88; DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.120.258467
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


