- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Microconvex probes provide more reliable outcomes in newborns undergoing lung USG: Study
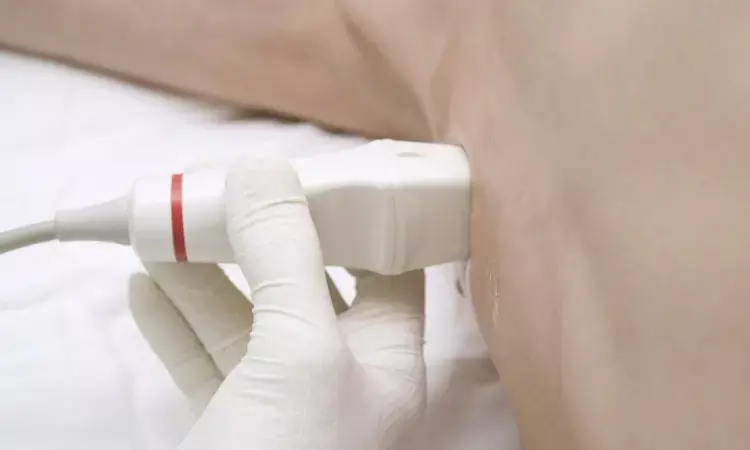
A new study by Lukas Aichhorn and team unveiled that the linear probe performs better with the microconvex probe than echo probes for lung ultrasonography in newborns. The findings of this study were published in the recent issue of journal of PLOS ONE.
In recent years, lung ultrasonography (LUS) has gained popularity in pediatric and neonatal critical care units. Many neonatologist performed lung ultrasound (NPLUS) protocols have been used in the regular environment to help in the identification of respiratory diseases, to provide guidance for operations like the insertion of chest tubes and for the administration of surfactants. The impact of probes used in ultrasound on lung ultrasound scores and picture quality is still unclear. As a result, this study compared the performance of three types of ultrasound probes in hemodynamically stable neonates, namely linear, microconvex and echo.
This prospective, randomized, blinded, comparative research was conducted between 2020 and 2022. The participants included were the hemodynamically stable newborns with nasal continuous positive airway pressure, a high flow nasal cannula, or no respiratory assistance. Lung ultrasonography with carried out with either an echo or a microconvex probe and the linear probe was the control. The main outcome measured was the NPLUS score. The additional outcome indicators were the number of B-lines, the thickness of the pleural line and subjective image quality. Furthermore, the association between NPLUS findings and clinical data was investigated.
An comprehensive analysis was conducted on 1584 video loops from a total of 66 newborns, whose mean corrected gestational age was 33.8 weeks and their weight was 1950g.
The NPLUS score was observed to be lower when using the echo- and microconvex probes in comparison to the linear probe with the corresponding coefficients of -1.09 and -2.95, respectively.
A reasonably good correlation was found between the NPLUS score and the pulse oximetric saturation/fraction of inspired oxygen ratio, with the greatest results obtained when utilizing the microconvex probe.
The findings help validate the current guidelines and also highlight the extent to which outcomes vary when alternative probes are utilized. The discrepancies revealed need careful interpretation of results, particularly when guiding therapy and presenting prognoses. Overall, the association between the NPLUS score and clinical characteristics will help to validate the usage of this diagnostic tool.
Source:
Aichhorn, L., Habrina, L., Werther, T., Berger, A., & Küng, E. (2024). Comparison of different types of ultrasound probes for lung ultrasound in neonates-A prospective randomized comparison study. In S. Yadav (Ed.), PLOS ONE (Vol. 19, Issue 7, p. e0306472). Public Library of Science (PLoS). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0306472
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


