- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
MRI effective for assessment of body composition in at-risk obese individuals
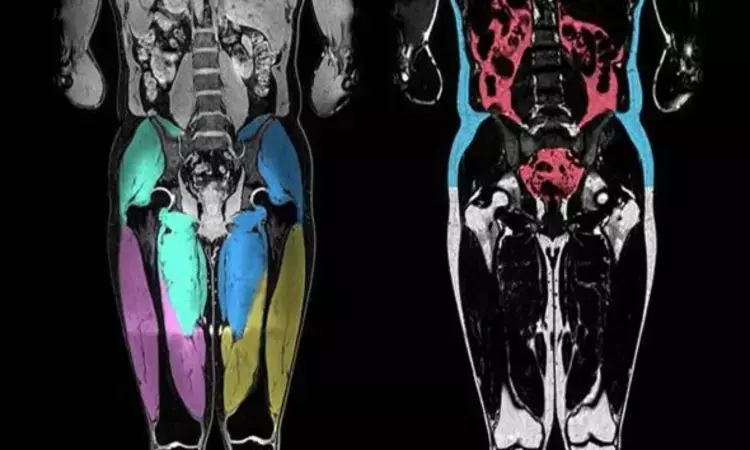
Spain: A team of researchers from Spain have reported magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to be just as effective as computed tomography (CT) for assessing body composition in obese patients at risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease (CVD), and nonalcoholic fatty liver. The findings were published in the most recent issue of Current Opinions of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism.
Juan Manuel Alcantara, the Public University of Navarre in Pamploma, Spain, and colleagues, however, note the additional benefit of MRI of not exposing patients to radiation.
There has been an exponential increase in the prevalence of obesity during the past years. The evaluation of human adipose tissue distribution enables the identification of diverse ectopic adipose tissue depots and helps to explain its relationship with cardiovascular health status.
For evaluating a person's body composition, there are non-imaging-based techniques -- such as bioelectrical impedance or skinfold thickness analysis, and other imaging modalities such as DEXA (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry) and ultrasound -- but clinicians have been turning more and more to MRI to evaluate fat distribution because of its high accuracy.
In the review, the researchers team summarized the current methods used in the assessment of human adipose tissue distribution. They discussed the relationship between ectopic adipose tissue distribution and the risk of developing CVDs and metabolic complications.
Key findings of the review:
· The reference instruments to assess human adipose tissue distribution nowadays are computed tomography and MRI.
· MRI is the preferred imaging technique and enables the measurement of variations in the distribution of body adipose tissue among different phenotypes and individuals. This technique has helped in better understanding the relationship between different ectopic adipose tissue depots and its relationship with cardiometabolic health among individuals.
"Although body composition can be assessed by simple techniques, these calculations can provide erroneous conclusions and results, needing complex interpretations when diverse metabolic situations are concomitantly engaged," the researchers wrote.
They added, "contrarily, medical imaging techniques (e.g. MRI) enable to objectively and unbiasedly measure changes that may occur during longitudinal studies (e.g. pharmacological drug interventions)."
"The review offers a useful primer for defining a patient's fatty tissue deposits and thus risk of disease," they concluded.
Reference:
Alcantara, Juan Manuel A.; Idoate, Fernando; Labayen, Idoia. Medical imaging in the assessment of cardiovascular disease risk. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 26(5):p 440-446, September 2023. | DOI: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000960
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


