- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Muscle mass measurement on DEXA predicts mortality in cardiac surgery patients: Study
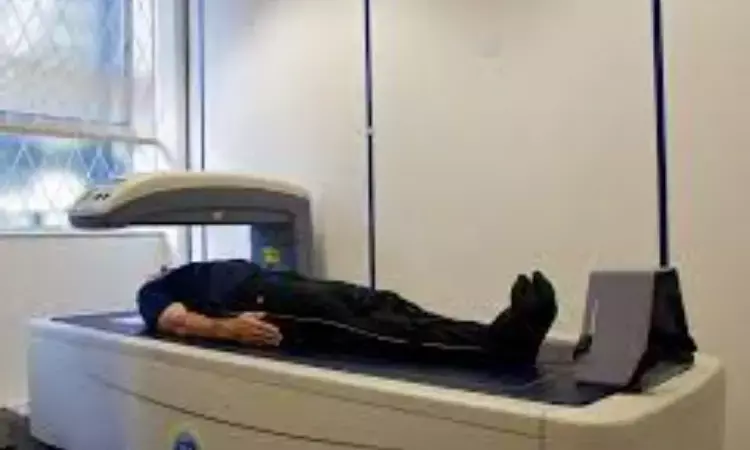
Montreal: A recent study in the American Heart Journal showed that in older cardiac surgery patients, the measurements of muscle mass on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) can help in predicting survival. The finding suggests measuring muscle mass provides valuable information for managing high-risk heart surgery patients.
"Lower-extremity muscle strength and dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA)-based muscle mass are objective indicators of sarcopenia that are independently predictive of all-cause mortality in older cardiac surgery patients," wrote the authors.
Aayushi Joshi, Centre for Clinical Epidemiology, Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, QC, and colleagues determined the prevalence and prognostic value of sarcopenia measured by DXA and physical performance tests in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve procedures.
The researchers prospectively enrolled adults undergoing cardiac surgery. They completed a questionnaire, physical performance battery, and a DXA scan (GE Lunar) to measure appendicular muscle mass indexed to height2 (AMMI). Based on European Working Group 2 guidelines, they were categorized as sarcopenic if they had low AMMI defined as <7 kg/m2 for men or <5.5 kg/m2 for women, and low muscle strength defined as 5 chair rise time ≥15 seconds.
The cohort consisted of 141 patients with a mean age of 69.7 ± 10.0 years and 21% females.
The research yielded the following findings:
- The prevalence rates of low AMMI, slow chair rise time, and sarcopenia (low AMMI and slow chair rise time) were 24%, 57%, 13%, respectively.
- The 4-year survival rate was 79% in the non-sarcopenic group as compared to 56% in the sarcopenic group.
- In the multivariable model, each standard deviation of decreasing AMMI and increasing chair rise time was associated with a hazard ratio for all-cause mortality of 1.84 and 1.79, respectively.
Sarcopenia (DXA-based low muscle mass and low muscle strength) is a valuable prognostic indicator of all-cause mortality after cardiac surgery, concluded the authors.
Reference:
The study titled, "Sarcopenia in cardiac surgery: Dual X-ray absorptiometry study from the McGill frailty registry," is published in the American Heart Journal.
DOI: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002870321001101
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


