- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Spectral CT improves detection of early-stage COVID-19
Chest CT has been used on a massive scale to help identify and evaluate suspected or confirmed COVID-19 cases, especially when RT-PCR testing was not available.
Researchers have found in a new study that the use of spectral CT with electron density imaging could improve the assessment of lung lesion extent in patients with early-stage coronavirus disease (COVID-19). The study has been published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
"In the present study," wrote Beatrice Daoud and colleagues at Antony's Private Hospital in France, "we report the first retrospective data from the spectral chest CT findings of patients with reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-confirmed COVID-19 (i.e., patients with positive RT-PCR test results)."
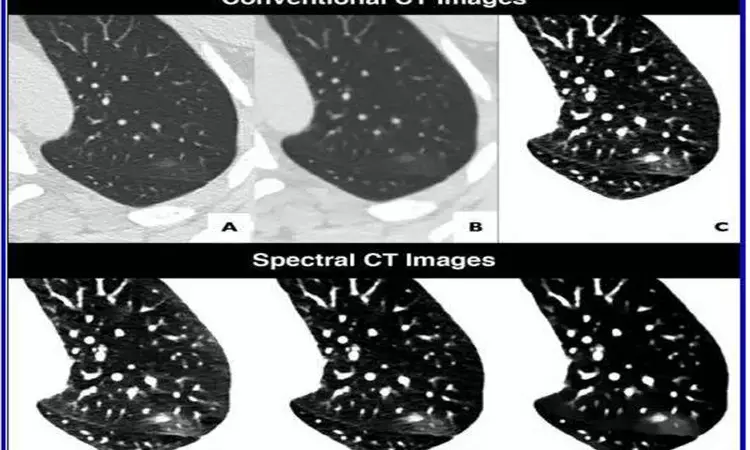
Since March 17, 2020, every patient who has had CT performed at the authors' institution for either suspected or RT-PCR-confirmed COVID-19 has undergone dual-layer detector-based spectral CT (IQon Spectral CT, Philips Healthcare). To evaluate the potential benefit of spectral imaging--electron density imaging, especially--two experienced thoracic radiologists reviewed the cases of four patients who each underwent two chest CT scans for confirmed COVID-19. Reconstructing the spectral CT images using the same standard soft kernel (filter B) and a similar iterative method that was used to acquire the conventional CT images, Daoud's team also compared initial conventional CT images with follow-up conventional CT images.
In all four patients, their pulmonary lesions (45 ground-glass opacities, overall) were more conspicuous on electron density images than on initial conventional CT images and were clearly confirmed on follow-up conventional CT images. Moreover, lesion extent, assessed via semiquantitative reporting scale denoting surface area involvement for each lobe, was easier to ascertain on electron density images. With Daoud and colleagues' results indicating electron density imaging improves early assessment of the extent of ground-glass opacities that could be missed by conventional CT, electron density showed the most promising results by enhancing the contrast of ground-glass opacities compared with the normal lung.
"We reviewed conventional chest CT images obtained with a parenchyma kernel and standard lung window setting, as is usually the case in everyday radiology practice," Daoud et al. explained, adding that they compared these images with conventional images obtained using a soft mediastinum kernel and standard lung window setting, conventional images obtained using a soft mediastinum kernel and narrow lung window setting, virtual low-monoenergy images, virtual high-monoenergy images, and electron density images.
"Our results suggest that the better ground-glass opacity visualization obtained using electron density imaging may be chiefly related to the increased visual noise in the image with soft kernel reconstruction and narrow lung window setting compared with electron density imaging, for which narrowing the window does not impair image quality," the authors of this AJR article concluded.
for further refrences please logon to :
http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23546
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


