- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Thermography effective imaging method for rheumatoid arthritis: Study
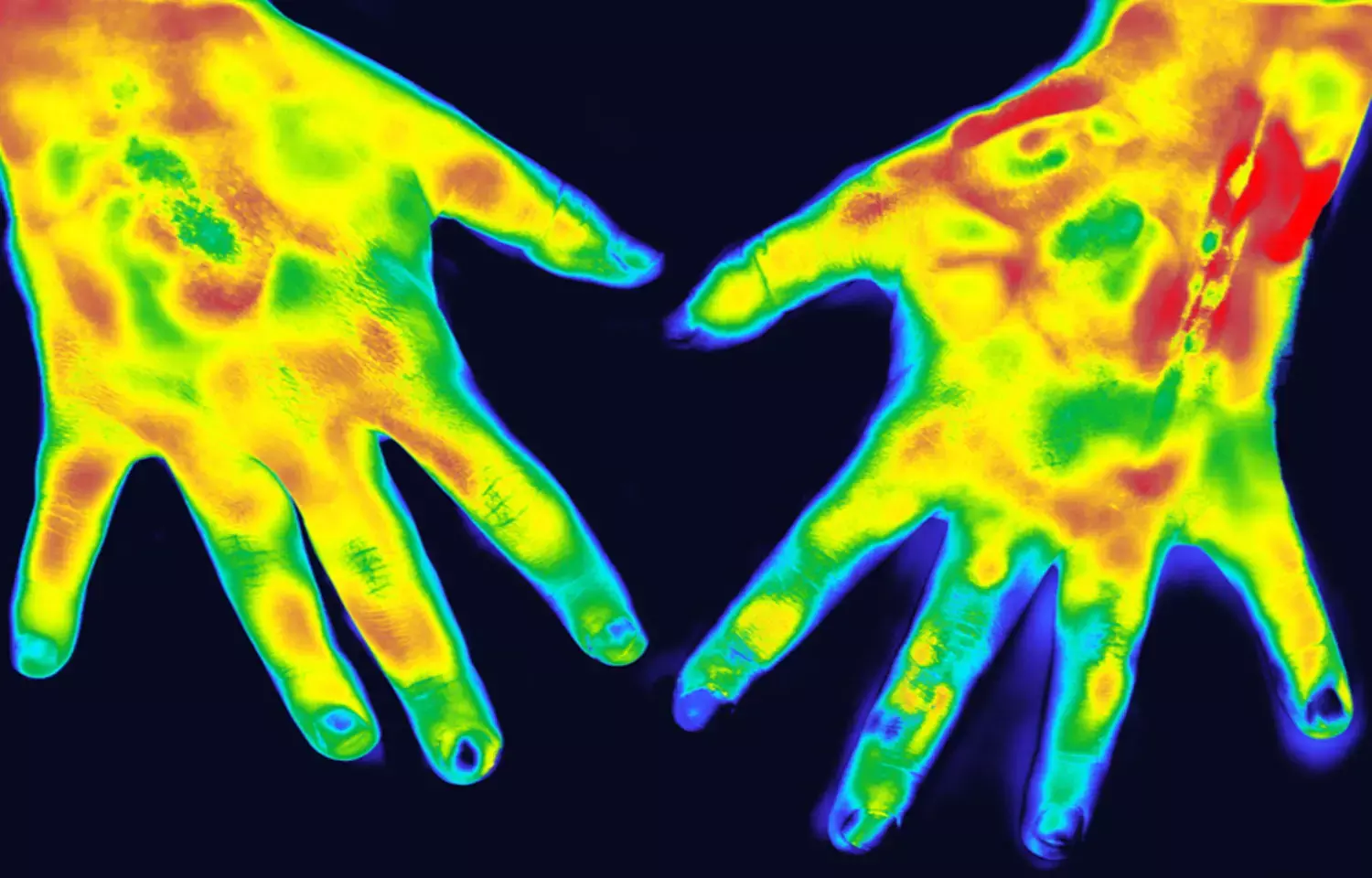
Singapore: When the ultrasound-detected joint inflammation is present, joints in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients have significantly higher temperature reading, according to a recent study. Swollen tender/non-tender joints versus non-swollen non-tender joints, showed a greater degree of ultrasound-detected joint inflammation, although their temperature readings were not significantly higher.
The results, published in the journal Clinical Radiology, indicate that thermal imaging or thermography is safe, non-invasive, and has high feasibility for use for RA patients.
Y.K. Tan, Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, and colleagues compared thermography with ultrasonography and clinical joint assessment in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
For the purpose, the researches sequentially performedThermography and ultrasonography (power Doppler (PD) and grey-scale (GS) joint inflammation scored semi-quantitatively 0–3) on both hands of 37 RA patients.
Using generalised estimating equations analysis, (a) thermographic parameters (TP) were compared between joints based on their PD and GS joint inflammation positivity/negativity status, while (b) TP and ultrasound-detected joint inflammation were compared between joints categorised by their clinical swelling/tenderness status.
Key findings of the study include:
- Comparing PD positive versus negative joints, the differences in mean values (95% CI) for TP including maximum (T max), minimum (T min), average (T avg), and T max minus T min (T max–min) temperatures (in °C) were 1.37, 0.91, 1.16, and 0.46, respectively.
- Comparing GS positive versus negative joints, the corresponding results for thermography were 1.09, 0.66, 0.86, and 0.45, respectively.
- The differences in mean values (95% CI) for ultrasound scores, but not for TP, were statistically significant for (a) swollen tender joints (PD: 0.67, GS: 0.86) and (b) swollen non-tender joints (PD: 0.46, GS: 0.83) when compared to non-swollen non-tender joints.
The study, "Thermography in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with ultrasonography and clinical joint assessment," is published in the journal Clinical Radiology.
DOI: https://www.clinicalradiologyonline.net/article/S0009-9260(20)30369-X/fulltext
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


