- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Barrett's neoplasia effectively managed with Radiofrequency ablation and endoscopic resection: Gut
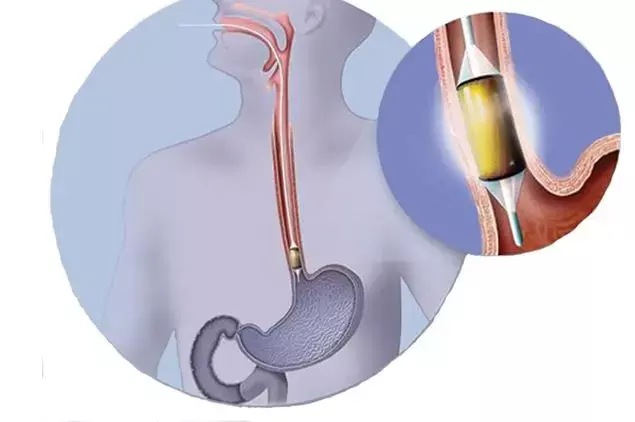
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)±endoscopic resection (ER) is effective for eradication of Barrett's related neoplasia and has remarkably low rates of dysplastic recurrence, according to recent study published in Gut, a BMJ journal. The team of researchers have further elaborated that, " Our data support more lenient Follow Up intervals, with emphasis on careful endoscopic inspection. Random biopsies from neosquamous epithelium and cardia are of questionable value."
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)±endoscopic resection (ER) is the preferred treatment for early neoplasia in Barrett's oesophagus (BE). Endoscopic eradication treatment (EET) is an established treatment approach for eradicating Barrett's oesophagus (BE) with early neoplasia. EET is generally a multimodal treatment consisting of endoscopic resection (ER) in case of visible lesions, followed by eradication of the residual flat BE segment, to minimise the risk of metachronous dysplasia. For the latter, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is the most commonly used technique. Current clinical guidelines unanimously recommend this effective and safe two-step approach as standard of care.Landmark studies consistently report excellent efficacy, with complete eradication of all neoplasia as well as complete eradication of all BE in 74%–98% of patients. However, the long-term durability remains poorly characterized.
So,a team of reserarchers aimed to report short-term and long-term outcomes for all 1384 patients treated in the Netherlands (NL) from 2008 to 2018, with uniform treatment and follow-up (FU) in a centralised setting.
Regarding the study design,Endoscopic therapy for early BE neoplasia in NL was centralised in nine expert centres with specifically trained endoscopists and pathologists that adhere to a joint protocol. Prospectively collected data are registered in a uniform database. Patients with low/high-grade dysplasia or low-risk cancer, were treated by ER of visible lesions followed by trimonthly RFA sessions of any residual BE until complete eradication of BE (CE-BE). Patients with ER alone were not included.
Results highlighted the following key facts.
- After ER (62% of cases; 43% low-risk cancers) and median 1 circumferential and 2 focal RFA (p25-p75 0–1; 1–2) per patient, CE-BE was achieved in 94% (1270/1348). Adverse events occurred in 21% (268/1386), most commonly oesophageal stenosis (15%), all were managed endoscopically.
- A total of 1154 patients with CE-BE were analysed for long-term outcomes.
- During median 43 months (22–69) and 4 endoscopies (1–5), 38 patients developed dysplastic recurrence (3%, annual recurrence risk 1%), all were detected as endoscopically visible abnormalities.
- Random biopsies from a normal appearing cardia showed intestinal metaplasia (IM) in 14% and neoplasia in 0%. A finding of IM in the cardia was reproduced during further FU in only 33%, none progressed to neoplasia.
- Frequent FU visits in the first year of FU were not associated with recurrence risk.
The team noted that after successful RFA treatment, the long-term risk for dysplastic recurrence is remarkably low: 1% per person year. All recurrences are detected as endoscopic abnormalities and not through random biopsies. There was no association between 3-monthly endoscopies in year 1 and improved patient outcomes.
"We suggest two important recommendations for post-treatment surveillance: (1) there is no need for frequent 3-monthly endoscopies during the first year after treatment; and (2) careful inspection is the most important aspect of follow-up endoscopies and random biopsies may be abandoned."the team opined.
For full article follow the link: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322615
Source:Gut
Dr Satabdi Saha (BDS, MDS) is a practicing pediatric dentist with a keen interest in new medical researches and updates. She has completed her BDS from North Bengal Dental College ,Darjeeling. Then she went on to secure an ALL INDIA NEET PG rank and completed her MDS from the first dental college in the country – Dr R. Ahmed Dental College and Hospital. She is currently attached to The Marwari Relief Society Hospital as a consultant along with private practice of 2 years. She has published scientific papers in national and international journals. Her strong passion of sharing knowledge with the medical fraternity has motivated her to be a part of Medical Dialogues.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


