- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Both Roux-en-Y gastric bypass bests sleeve gastrectomy for weight reduction, reveals research
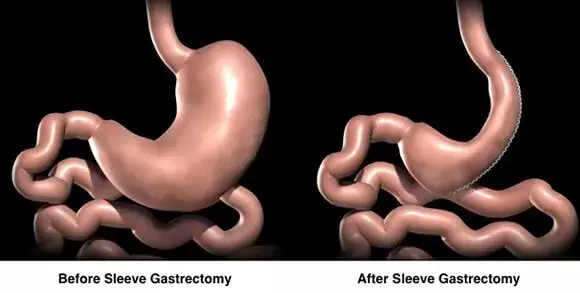
A new study published in the journal of The Lancet Diabetology and Endocrinology revealed that with 68% of individuals obtaining at least 50% excess weight reduction, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass was determined to be the most successful procedure for treating extreme obesity. This is in contrast to 41% for sleeve gastrectomy and 25% for adjustable gastric banding.
Bariatric and metabolic surgery can result in a 20% to 30% reduction in overall weight. According to trials, obesity-management pharmaceuticals can reduce overall weight loss by up to 24%. However, this may be less in real-world situations. The long-term effects and acceptability of these medications are unknown.
Both bariatric and metabolic surgery can lower the health risks associated with extreme obesity; however, it is unclear which procedure is more cost-effective or efficient. Thus, this study was set out to compare sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric banding, and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in individuals who were extremely obese.
A total of 12 UK hospitals participated in the pragmatic, multi-center, open-label, randomized controlled study known as By-Band-Sleeve. Adults (≥18 years old) who satisfied national requirements for bariatric and metabolic surgery were eligible participants. When sleeve gastrectomy became popular in the UK, two and a half years after the study's inception, a two-group experiment was expanded to a three-group trial.
Weight and quality-of-life (EQ-5D utility score) at 3 years were co-primary objectives. Sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass were deemed more effective than adjustable gastric banding and sleeve gastrectomy more effective than Roux-en-Y gastric bypass if the percentage of patients who achieved at least 50% excess weight loss was non-inferior and quality-of-life was superior.
A total of 1,351 individuals were randomly allocated between January 16, 2013, and September 27,2019. 1,346 of them were included in this research, while 5 withdrew their permission.
There were 1,346 participants, of whom 462 (34%) underwent a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, 464 (34%) underwent an adjustable gastric banding, and 420 (31%) underwent a sleeve gastrectomy. Surgery was performed on 1,183 (88%) of the subjects.
At least 50% excess weight reduction was attained by 276 (68%) of 405 patients in the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass group, 97 (25%) of 383 participants in the adjustable gastric banding group, and 141 (41%) of 342 people in the sleeve gastrectomy group.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, and sleeve gastrectomy all had mean EQ-5D ratings of 0·72, 0·62, and 0·68, respectively. After surgery, 1,651 adverse events were documented. Overall, it is suggested that patients who choose metabolic and bariatric surgery have Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Reference:
By-Band-Sleeve Collaborative Group. (2025). Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, or sleeve gastrectomy for severe obesity (By-Band-Sleeve): a multicentre, open label, three-group, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. Diabetes & Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(25)00025-7
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


