- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Diabetes: Bariatric surgery bests medical treatment in improving kidney disease
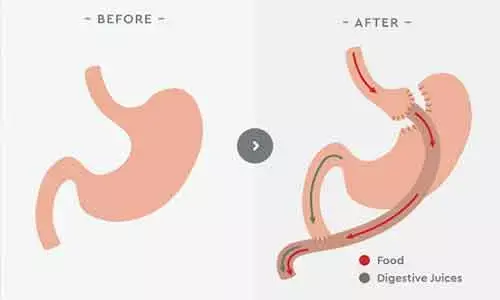
Delhi: Gastric bypass is more effective than the best medical treatment (BMT) in improving kidney disease in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), a recent study in the journal JAMA Surgery. It found roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) to be a safe and more effective means of achieving remission of early-stage CKD and albuminuria than BMT treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes, obesity, and microalbuminuria.
The study is significant as in T2D patients early-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD) characterized by microalbuminuria is associated with future cardiovascular events, progression toward end-stage renal disease, and early mortality.
Ricardo Vitor Cohen, The Center for Obesity and Diabetes, Oswaldo Cruz German Hospital, São Paulo, Brazil, and colleagues conducted the study to compare the albuminuria-lowering effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery vs best medical treatment in patients with early-stage CKD, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
The researchers conducted a randomized, single-center trial of 100 patients with T2D, obesity, and microalbuminuria (urinary albumin-creatinine ratio [uACR] >30 mg/g and estimated glomerular filtration rate >30 mL/minute/1.73 m2). They were randomly assigned to BMT or RYGB (51 to RYGB and 49 to best medical care).
Key findings of the study include:
- Remission of albuminuria occurred in 55% of patients after best medical treatment and 82% of patients after RYGB, resulting in CKD remission rates of 48% after best medical treatment and 82% after RYGB.
- The geometric mean uACRs were 55% lower after RYGB (10.7 mg/g of creatinine) than after best medical treatment (23.6 mg/g of creatinine).
- No difference in the rate of serious adverse events was observed.
"After 24 months, RYGB was more effective than best medical treatment for achieving remission of albuminuria and stage G1 to G3 and A2 to A3 CKD in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity," concluded the authors.
The study, "Effect of Gastric Bypass vs Best Medical Treatment on Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial," is published in the journal JAMA Surgery.
DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.0420
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


