- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Weight loss: Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty effective option for obese patients: Lancet
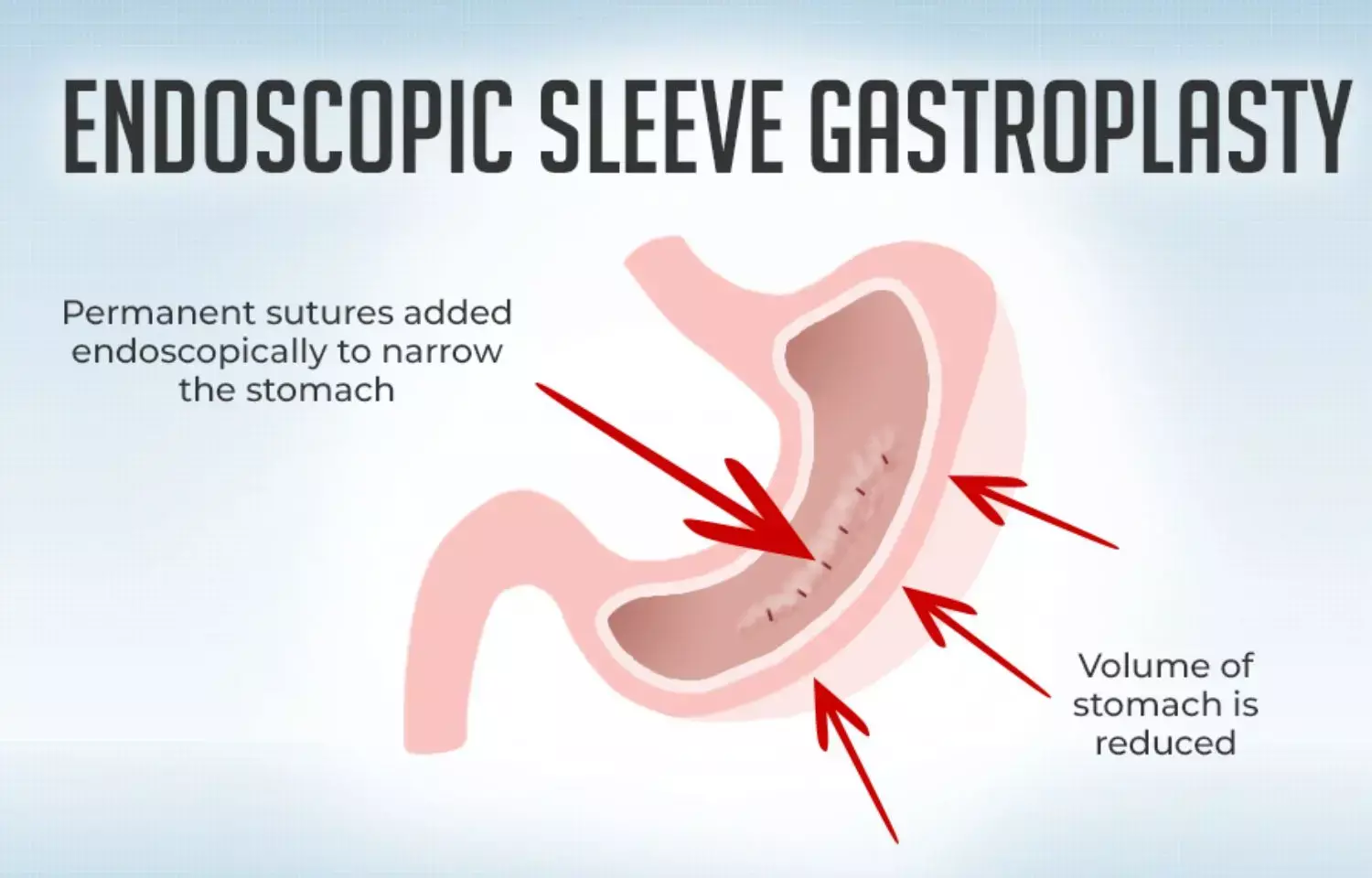
USA: A new study in The Lancet found that endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is a safe intervention leading to significant weight loss and improvement in metabolic comorbidities in patients with class 1 or class 2 obesity.
Globally, Obesity has reached epidemic proportions. Obesity is a serious, chronic disease that leads to an increased risk of mortality and morbidity. It is characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat. The body Mass Index (BMI) estimates the level of body fat based on height and weight.BMI is used as an indicator of the risk of developing obesity-related health problems. Class 1 (low-risk) obesity( BMI is 30.0 to 34.9) and Class 2 (moderate-risk) obesity (BMI is 35.0 to 39.9).
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is an endoluminal, organ-sparing therapy for obesity, with wide global adoption. It is a minimally invasive, endoscopic weight loss procedure, reducing the risk of operative complications and allowing a quick return to daily activities.
Prof Barham Abu Dayyeh, Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, USA, and his team conducted a randomized clinical trial to explore the efficacy and safety of ESG with lifestyle modifications compared with lifestyle modifications alone.
For the trial, researchers enrolled individuals aged 21–65 years with class 1 or class 2 obesity, who agreed to comply with lifelong dietary restrictions. Participants were randomly assigned (1:1•5) to ESG with lifestyle modifications (ESG group, n-85) or lifestyle modifications alone (control group, n-124), with potential retightening or crossover to ESG, respectively, at 52 weeks. Lifestyle modifications included a low-calorie diet and physical activity. Participants in the primary ESG group were followed up for 104 weeks.
The primary endpoint at 52 weeks was the percentage of excess weight loss (EWL), with excess weight being that over the ideal weight for a BMI of 25 kg/m2. Secondary endpoints included changes in metabolic comorbidities between the groups. Analyses were done on a per-protocol basis and a modified intention-to-treat basis.
Key findings from the trial data,
• The mean percentage of EWL was 49•2% for the ESG group and 3•2% for the control group.
• The mean percentage of total body weight loss was 13•6% for the ESG group and 0•8% for the control group.
• 77% of the participants in the ESG group reached 25% or more EWL compared with 12% in the control group.
• 80% of participants in the ESG group had an improvement in one or more metabolic comorbidities, whereas 12% worsened, compared with the control group in which 45% of participants had similar improvement, whereas 50% worsened.
• At 104 weeks, 68% of participants in the ESG group maintained 25% or more of EWL.
• ESG-related serious adverse events occurred in 2% of participants, without mortality or need for intensive care or surgery.
The authors conclude that ESG is a safe, effective, and durable procedure and should be considered as a synergistic weight loss intervention for patients with class 1 or class 2 obesity. "ESG is a safe intervention that resulted in significant weight loss, maintained at 104 weeks, with important improvements in metabolic comorbidities," they wrote.
The ESG procedure will prove to be an important tool for both surgeons and gastroenterologists to help address the global obesity epidemic, the authors wrote.
Reference:
Prof Barham K Abu Dayyeh, Fateh Bazerbachi, Eric J Vargas, Reem Z Sharaiha, Prof Christopher C Thompson, Bradley C Thaemert, et al. Published: July 28, 2022. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01280-6
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


