- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Plate-assisted reduction during intramedullary nailing of tibia shaft fractures may lower risk of nonunion or infection: Study
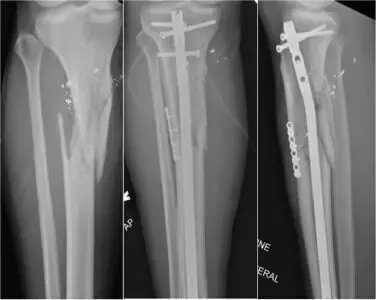
Plate-assisted reduction during intramedullary nailing of tibia shaft fractures may lower risk of nonunion or infection suggests a new study published in the European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology
The purpose of this meta-analysis is to analyse the literature on plate-assisted reduction during intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures and to compare the rates of infection and nonunion.
The databases Medline, Embase, and Web of Science were searched from inception to February 2022 for literature comparing plate-assisted reduction during intramedullary nailing of extra-articular tibia fractures to standard, closed means of reduction. Data were extracted and pooled in a random effects meta-analysis for the primary outcomes of nonunion and infection risk.
RESULTS
Five comparative studies were identified including 520 total patients, of which 151 underwent tibial nailing with the use of plate-assisted reduction with an average follow-up time of 17.9 months. Approximately two-thirds of patients retained the plate used to assist reduction during intramedullary nailing (102 of 151). Pooled analysis of the infection rates found no significant difference with plate-assisted intramedullary nailing (Risk Ratio [RR] 0.90, 95% CI 0.49-1.65, p = 0.72), and for nonunion rates, there was also no significant difference with plate-assisted intramedullary nailing (Risk Ratio [RR] 0.80, 95% CI 0.40-1.60, p = 0.53).
Plate-assisted reduction during intramedullary nailing of tibia shaft fractures was not associated with an increased risk for nonunion or infection, and can be safely applied as an adjunct for reduction in challenging fracture patterns, without the need for later removal. However, evidence is quite limited and further investigation into the use of provisional plating as a technique is needed as its use in intramedullary nailing continues to expand.
Reference:
Gouveia, Kyle, et al. "Plating as a Reduction Aid Prior to Intramedullary Nailing of Tibia Fractures: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis." European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology : Orthopedie Traumatologie, 2023.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


