- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Positive subareolar tissue biopsy indicative of residual carcinoma in excised nipples: Study
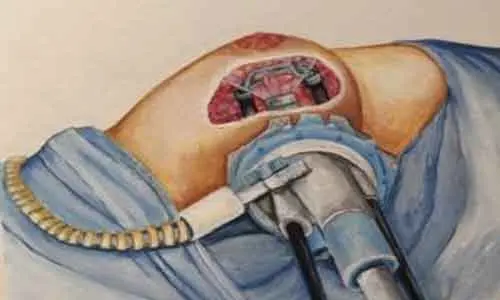
USA: A new study shows that In 51% of instances, a positive subareolar tissue biopsy indicates residual cancer in the removed nipples. The findings of this study were published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
While nipple-sparing mastectomy has superior aesthetics, body image, patient satisfaction, and psychological impacts, it is related to postoperative morbidity and oncologic risk, notably residual malignancy inside the preserved nipple-areola complex. To reduce the danger of concealed cancer within the preserved nipple, subareolar tissue is evaluated during nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM). A positive subareolar tissue biopsy usually necessitates nipple excision. As a result, Lucy X Ma and colleagues undertook this study to determine the parameters associated with a positive subareolar tissue biopsy, the rate of residual malignancy in consecutive nipple excisions, and the utility of intraoperative frozen section subareolar tissue biopsy.
Over a 5.5-year period, researchers identified 1,026 consecutive NSMs with individually submitted subareolar tissue samples for this study. The clinicopathologic data were extensively examined. The researchers looked at the rates of concordance between the subsequent nipple and subareolar tissue biopsy excisions, as well as the rates of IOF diagnosis and permanent control diagnosis.
The findings of this study were as follow:
1. A positive subareolar tissue biopsy was found in 7.2% of instances with therapeutic NSM.
2. A positive subareolar tissue biopsy was linked with multifocal/multicentric illness, lymphovascular invasion, and nodal involvement.
3. Thirty-nine of 41 instances with positive subareolar biopsies had nipple excisions, with 20 (51%) revealing residual cancer.
4. There was a disagreement between the IOF and permanent diagnosis in 9 (3.3%) of all IOF samples, primarily due to false negatives.
In conclusion, a positive subareolar tissue biopsy on persistent pathology, on the other hand, would necessitate a second revision treatment, which might result in less desirable cosmetic effects due to skin scarcity.
Reference:
Ma LX, Michaels AY, Ginter PS. Subareolar Tissue Biopsy Predicts Occult Nipple Involvement in Nipple-Sparing Mastectomies. Am J Clin Pathol. 2022 Feb 3;157(2):266-272. doi:10.1093/ajcp/aqab126. PMID: 34519762.
Keywords: cosmetic nipple surgery, mastectomy, clinical pathology, cancer residue, subareolar tissue biopsy, frozen section, malignancy, breast cancer, American Journal of Clinical Pathology
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


