- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sealing fistulas with regenerative immiscible bioglue
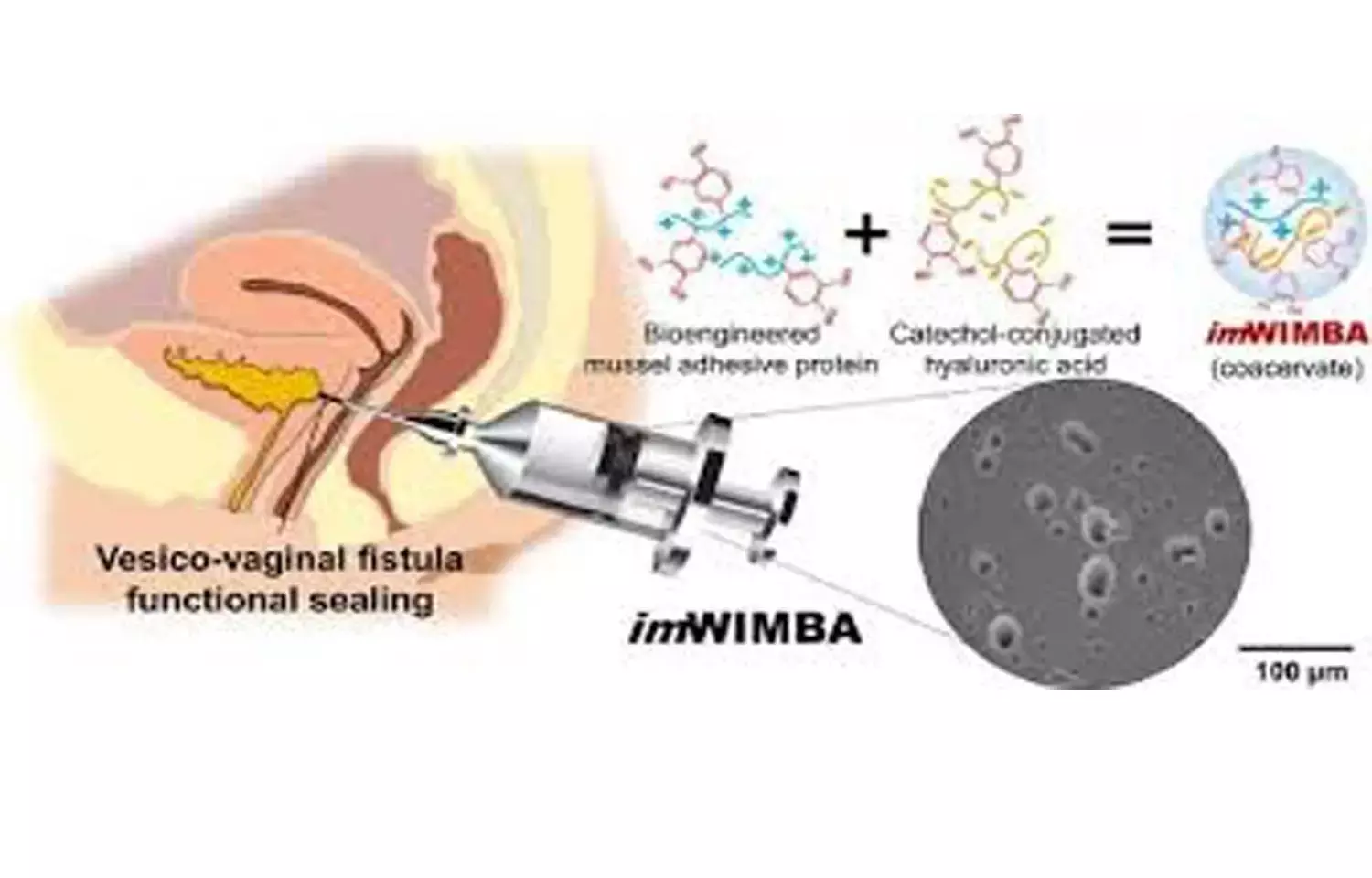
A Korean research team has recently developed an innovative vesico-vaginal fistula treatment method using the mussel adhesive protein (MAP) that can effectively seal fistulas in organs even when exposed to urine.
Professor Hyung Joon Cha, Dr. Hyo Jeong Kim (currently at Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology), and Dr. Tae Yoon Park of POSTECH's Department of Chemical Engineering with Professor Seok Ho Kang of the Department of Urology at Korea University School of Medicine and Professor Jong Hyun Pyun of the Department of Urology at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital have together improved the underwater adhesive using mussel protein and applied it to a pig model that simulated a vesico-vaginal fistula. As a result, it was confirmed that the fistula was sealed much quicker and more effectively than the conventional treatment method that uses sutures, and its treatment efficacy was proven to be superior.
Fistula refers to an abnormal opening between the organs consisting of two spaces, such as blood vessels or intestines. Among them, the bladder is in contact with various organs such as the intestine, uterus, and vagina in the abdominal cavity and a fistula here causes urine leakage that can induce serious complications such as fecal incontinence or bladder inflammation. This not only impairs the patients' quality of life, but female fistulas are stigmatized in many developing countries, affecting the human rights and dignity of women.
Currently, a physical suture method is typically used for treating vesico-vaginal fistulas. However, this technique has multiple limitations since the surgeries are difficult and the repetitive contraction and expansion of the bladder damages the tissue, which results in delayed healing of the wound.
To this, the POSTECH-Korea University joint research team developed a formulation in 2016 that uses the phase separation property of mussel adhesive proteins to develop a water-immiscible bioadhesive that does not dissolve in body fluids like blood or urine and exhibits excellent underwater adhesion. Moving further, the researchers conducted experiments on a pig model with vesico-vaginal fistula with improved water-immiscible bioadhesive for practical applications in clinical practice.
The joint research team used a liquid-liquid phase separation formulation with thixotropy to develop the adhesive so that the high-viscosity liquid adhesive can be accurately delivered to the fistula area via a thin syringe. In addition, after the fistula is sealed, it is designed so that it does not flow out or fall out of the fistula.
The researchers confirmed that by maximizing the concentration of catechol - which acts as an important functionality in underwater adhesion - the stability of the adhesion is increased even more in the presence of body fluids. It was also confirmed that the fistula's closing force continued to be maintained in the bladder, an organ that repeatedly contracts and expands, thanks to the flexible property of a protein-based adhesive, and the protein adhesive biodegrades and the fistula naturally regenerates.
With no immune response or inflammation observed around the sealed fistula, low surgical difficulty, and easy access to large quantities of materials, the adhesive is anticipated to be used widely in developing countries with poor medical facilities. The water-immiscible mussel protein-based bioadhesive (imWIMBA) has undergone a technology transfer to Nature Gluetech Co., Ltd. and is currently being commercialized.
"We have confirmed the mussel adhesive protein - a technology that originated in Korea - as an effective vesico-vaginal fistula treatment method by applying it to an actual vesico-vaginal fistula of a large animal model," explained Professor Hyung Joon Cha of POSTECH. "It is anticipated to be successfully applicable to fistulas and perforations in other similar environments."
"Vesico-vaginal fistula is a disorder difficult to treat and it significantly impacts the patient's quality of life," remarked Professor Seokho Kang of Korea University. "We expect the newly developed treatment method to be applicable to minimally-invasive surgical methods such as robotic surgery and endoscopic surgery as well as open surgeries in the future based on its excellent water-immiscibility and underwater adhesion.
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


