- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study doesn't support DJBL for weight loss in patients with metabolic syndrome
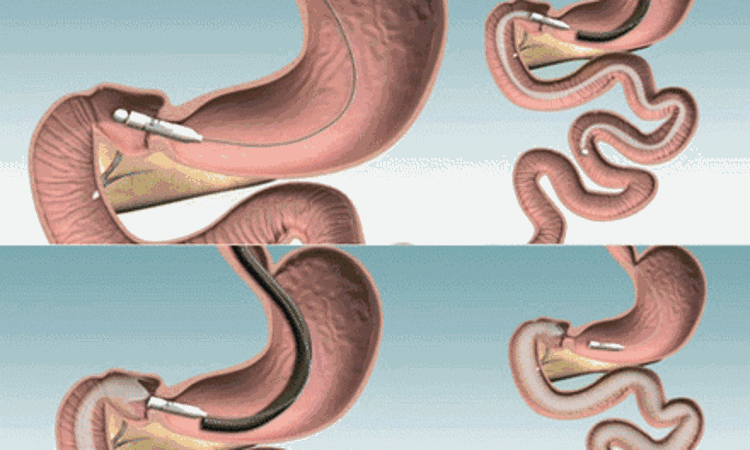
Efficacy and Safety of the Duodeno-Jejunal Bypass Liner in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome was assessed by researchers in ENDOMETAB trial and found the results don't support its routine use for weight loss and blood sugar control in metabolic syndrome.
Conventional medical care for metabolic syndrome involves combination of dietary advice, physical activity and psychological treatment which offers only limited results, both in weight reduction and comorbidities. Bariatric surgery allows however a significant and sustained weight loss in the majority of cases, and a decrease in the frequency and severity of co-morbidities, including type 2 diabetes, and decreased mortality including cardiovascular. Different techniques that may replace surgery are currently being developed.
In ENDOMETAB trial researchers assessed the safety and efficacy of DJBL (duodeno-jejunal bypass liner), an endoscopic device for treating obesity and related disorders. The trial details were published on Annals of Surgery in 25, November 2020.
It was a multicenter, randomized controlled trial involving 82 patients (67.5% female, 48.8% with diabetes) with metabolic syndrome (MS). Researchers designed the study with an objective to compare the efficacy and safety of 12-month implantation of a duodeno-jejunal bypass liner (DJBL) with conventional medical care. They determined primary endpoints as the rate of resolution of Metabolic Syndrome at 1 year, measured by the frequency of patients without MS at 12 months. The secondary endpoints assessed were body mass index (BMI), glucose control, blood pressure, and lipids, assessed at 12 months after implantation, and again, at 12 months after the removal of DJBL.
KEY FINDINGS OF THE TRIAL WERE:
Among 82 patients 6 in DJBL patients (12%)and 3 in conventional care (10%) reached the primary endpoints.
Researchers found patients in the DJBL group experienced greater BMI loss when compared with the control group.
They also found significant changes in HbA1c levels of patients in the DJBL group than those in the control group.
However, there were no statistically significant differences noted at 12 months after the removal of the DJBL.
In the DJBL group, 39% of patients experienced at least one device-related serious adverse event, which was classified as Grade III Dindo-Clavien in 22%, and required premature device explantation in 16%.
The ENDOMETAB trial findings showed a transient clinical benefit of DJBL for a year when the device was in place with 39% device related serious adverse events.
The authors concluded, "These results do not support the routine use of DJBL for weight loss and glucose control in patients with MS".
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


