- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Weight-Loss Surgery Significantly Cuts Risk of Severe Complications in obese COVID-19 Patients
NEWBERRY, FL - Adults with obesity who had weight-loss surgery and achieved substantial weight loss prior to contracting COVID-19 reduced their risk for developing severe outcomes from the infection by 60% compared to those who did not have surgery, according to a new Cleveland Clinic study published online today in the journal JAMA Surgery. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), having obesity increases the risk of severe illness from COVID."
This is an important study that shows that patients with obesity who had bariatric surgery and subsequently developed COVID-19 had greatly reduced their risk for hospitalization, supplemental oxygen, and severe infection compared to similar patients that did not have bariatric surgery," said Shanu N. Kothari, MD, president of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), who was not involved in the study. "This timely study should serve as further motivation for patients and their doctors to treat the disease of obesity before potentially having to treat its dangerous consequences."
Obesity is linked to more than 40 diseases including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, stroke, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis and at least 13 different types of cancer. The CDC reports that from 1999 –2000 through 2017 –2018, the prevalence of obesity in the U.S. increased from 30% to 42% and severe obesity increased from 4.7% to 9.2%.M
etabolic/bariatric surgery has been shown to be the most effective and durable treatment for severe obesity, resulting in significant weight loss and resolution or improvements in diabetes, heart disease, sleep apnea and many other diseases. The safety profile of laparoscopic bariatric surgery is comparable to some of the safest and most commonly performed surgeries in the U.S. including gallbladder surgery, appendectomy and knee replacement.
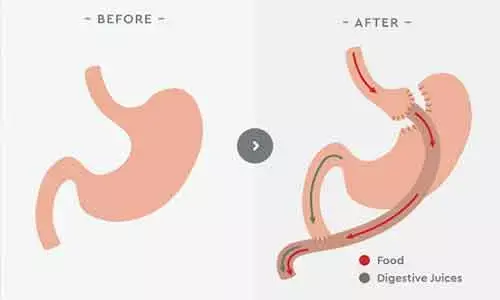
In estimated 256,000 bariatric surgeries were performed in 2019, according to the ASMBS, which represents less than 1 percent of the currently eligible surgical population by BMI. Nearly 60% were sleeve gastrectomies, an increasingly popular procedure that involves removing most of the stomach and shaping the remainder into a tube or sleeve, restricting the amount of food it can hold. About 18% of procedures were gastric bypass.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/fullarticle/2787613?guestAccessKey=bae9556b-f9c4-4a3d-b4ec-f937c39566c1&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=122921
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


