- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Formula based on X ray chest and ultrasound may help place CVC tip successfully during axillary vein cannulation
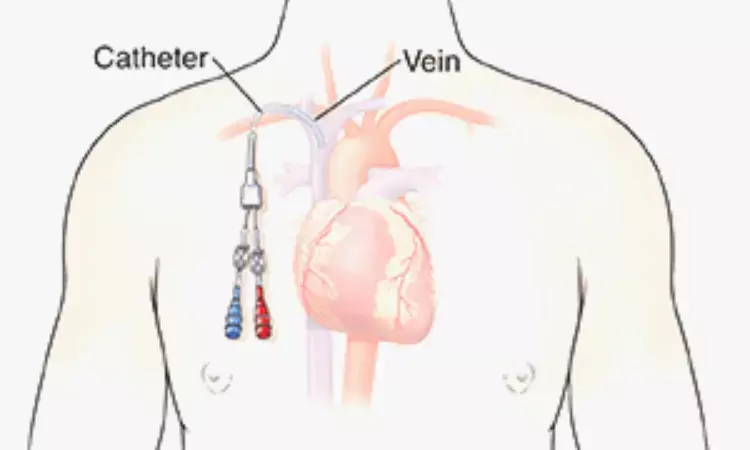
Maintaining a central venous catheter tip in a secure position is crucial. There are a number of methods for calculating an approximate catheter insertion length in both the subclavian and internal jugular veins. However, the techniques for calculating the axillary route insertion length have not been verified. A recently published research tested a straightforward approach to estimating catheter insertion length to see whether it reliably forecasts where the catheter tip should be placed.
The axillary vein (AxV) was successfully cannulated in 60% of the 102 patients who needed central venous cannulation before surgery. By measuring the clavicular length (A), the vertical distance between the sternal head and carina (B), and the perpendicular distance from the skin to the AxV (Y), we were able to determine the insertion length. The precise location of the tip (2 cm above the carina to 0.5 cm below it) was evaluated using a postoperative CXR. Successful placement of the central venous catheter (CVC) in terms of the right location of the catheter tip was the main result of the research when the insertion length was predicted using the formula mentioned above. Eighty-three percent of the time, the location was just right. Female patients (P = 0.03) and shorter patients (P = 0.01) had a significantly greater accuracy rate. High levels of concordance were shown via a Bland-Altman scatter plot.
In this feasibility research, the catheter tip was successfully placed in the target zone in 50 out of 60 patients (83.33%) when the insertion length was predicted beforehand. We were able to get a good idea of how long the insertion would need to be by utilizing the scale on the CXR to figure it out. The authors find that 83.33 percent of the time, the CVC tip may be successfully placed using the calculation based on a CXR and ultrasonography.
Reference –
Naik, Srikanth; Pappu, Ameya; Sarathkumar, M.S; Ramachandran, Rashmi; Arora, M.K.1; Trikha, Anjan; Singh, Preet M.2; Anand, Rahul Kumar; Das, Chandan J.3; Rewari, Vimi. Determination of the optimal length of insertion for central venous catheterization via axillary vein cannulation using preoperative chest X-ray- A prospective feasibility study. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology 39(2):p 215-219, Apr–Jun 2023. | DOI: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_223_21
MBBS, MD (Anaesthesiology), FNB (Cardiac Anaesthesiology)
Dr Monish Raut is a practicing Cardiac Anesthesiologist. He completed his MBBS at Government Medical College, Nagpur, and pursued his MD in Anesthesiology at BJ Medical College, Pune. Further specializing in Cardiac Anesthesiology, Dr Raut earned his FNB in Cardiac Anesthesiology from Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Delhi.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


