- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Saline injection prior to interscalene block protects phrenic nerve, study finds
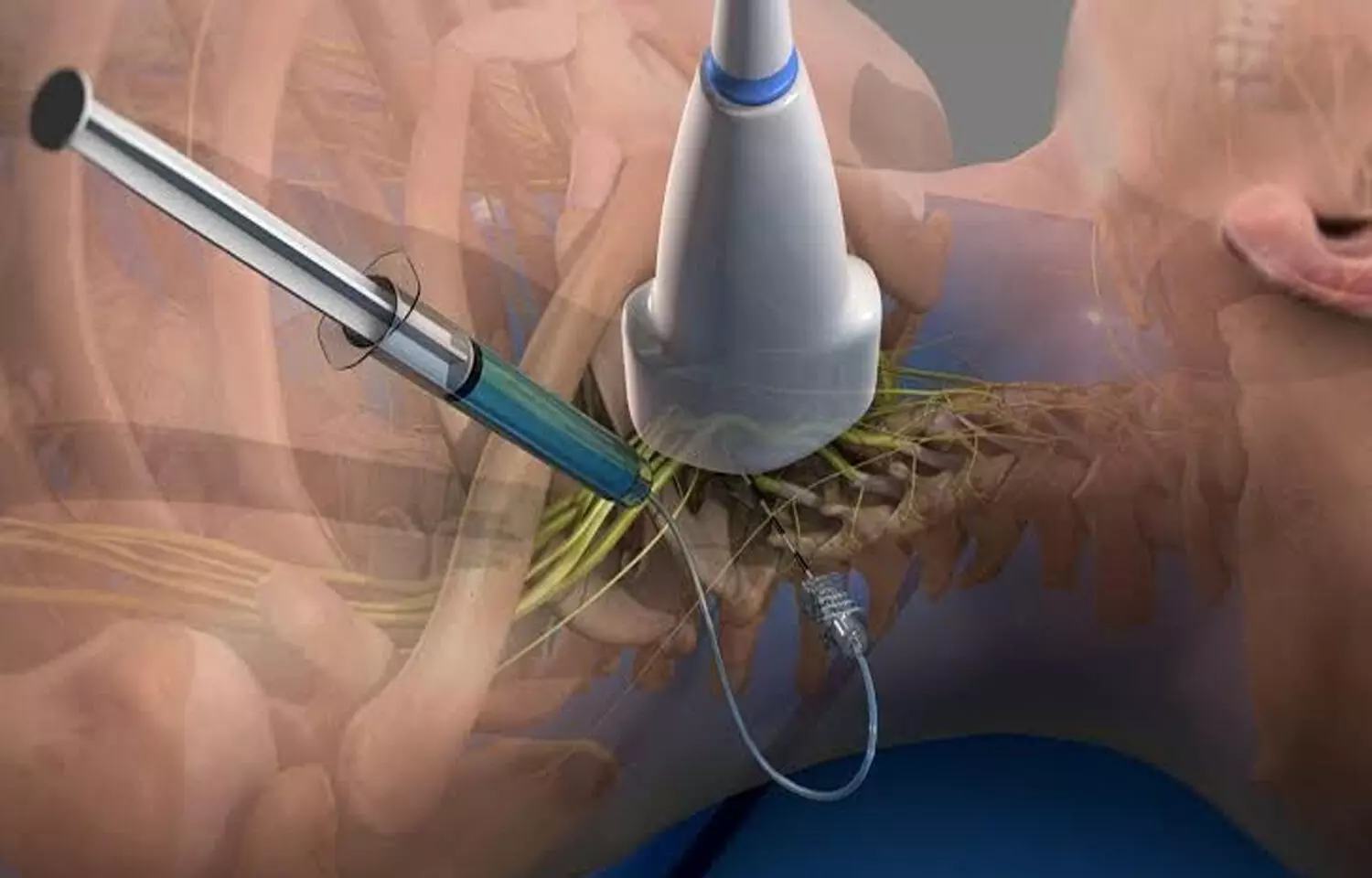
Ireland: A recent study published in the Indian Journal of Anaesthesia brought out the fact that before an ultrasound-guided interscalene block, administering saline injection anterior to the region of interest reduced the incidence of phrenic nerve palsy. This study was performed by doctors from Ireland and focused to reduce the risk of palsy during an interscalene block.
A total of 36 patients were randomly grouped into group C (conventional) and group S (saline). Both groups had an ultrasound-guided interscalene block with 20 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine. But in group S, before the interscalene block was performed, 10 ml of normal saline was administered anterior to the anterior scalene muscle. Diaphragmatic ultrasound pre-and post-operatively was performed to document phrenic palsy. Additionally, to evaluate baseline and postoperative pulmonary function tests bedside spirometry was used.
Key highlights of the study
• A 10 mL injection of normal saline into the front scalene muscle, prior to interscalene block significantly decreased the incidence of Hemi-diaphragmatic palsy.
• The study also stated that there was no marked difference between the two groups in post-operative analgesia, subjective sensation of dyspnea, and patient satisfaction.
• According to the findings, injecting 10 mL of normal saline prior to the administration of local anesthesia reduces phrenic nerve palsy by 50%.
In conclusion, the lead of the study Dr. Srinivasan stated "the saline technique demonstrated a non-inferior analgesia as the conventional interscalene block technique while showing a significant reduction in the incidence of Hemi-diaphragmatic palsy."
For further insight
Srinivasan, K., Ryan, J., Snyman, L., O'Brien, C., & Shortt, C. (2021). Can saline injection protect phrenic nerve? – A randomised controlled study. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 65(6), 445. https://doi.org/10.4103/ija.ija_182_21
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.