- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Burnout making doctors prescribe wrong medicines: JAMA Meta-Analysis on 43,000 Doctors
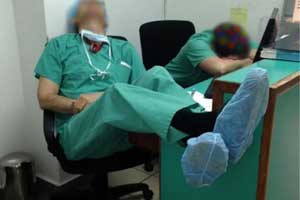
Another worrying finding of the study is that in junior doctors in particular, burnout increases the likelihood of lower professional standards by 3.5 times
It found that burnout in doctors has devastating consequences on the quality of care they deliver, researchers said.
Burnout also doubles the likelihood of lower professional standards, such as not following set guidelines or malpractice, they said.
It may have an impact on dropping patient satisfaction, said Maria Panagioti from the University of Manchester in the UK, who led the study.
The study found that patient satisfaction is three times more likely to be lower when doctors are physically, emotionally and mentally exhausted -- core signs by which experts identify burnout.
It also found that in junior doctors in particular, burnout increases the likelihood of lower professional standards by 3.5 times.
"This meta-analysis provides a snapshot of what happens to patients when their doctors are burnt out," Panagioti said.
"We show conclusively that the provision of safe, high-quality patient care is severely compromised when doctors are physically, emotionally and mentally exhausted," she said.
Researchers noted that this is not the fault of doctors.
It is caused by a combination of factors including high workload, the way teams work together and the absence of measures which improve wellbeing, they said.
"But it is also about a performance culture which in recent years has become more prevalent in the medical profession," said Panagioti.
"Doctors are increasingly being asked to be superhuman when they are not. They need care and attention that anyone would need when under such enormous pressure and that is just not happening," she said.
London: Doctors with burnout are twice as likely to prescribe the wrong medicines and make incorrect diagnoses, a large-scale study has found. The study, published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine, looked at 47 research papers which together analysed the responses of 43,000 doctors.
It found that burnout in doctors has devastating consequences on the quality of care they deliver, researchers said.
Burnout also doubles the likelihood of lower professional standards, such as not following set guidelines or malpractice, they said.
It may have an impact on dropping patient satisfaction, said Maria Panagioti from the University of Manchester in the UK, who led the study.
The study found that patient satisfaction is three times more likely to be lower when doctors are physically, emotionally and mentally exhausted -- core signs by which experts identify burnout.
It also found that in junior doctors in particular, burnout increases the likelihood of lower professional standards by 3.5 times.
"This meta-analysis provides a snapshot of what happens to patients when their doctors are burnt out," Panagioti said.
"We show conclusively that the provision of safe, high-quality patient care is severely compromised when doctors are physically, emotionally and mentally exhausted," she said.
Researchers noted that this is not the fault of doctors.
It is caused by a combination of factors including high workload, the way teams work together and the absence of measures which improve wellbeing, they said.
"But it is also about a performance culture which in recent years has become more prevalent in the medical profession," said Panagioti.
"Doctors are increasingly being asked to be superhuman when they are not. They need care and attention that anyone would need when under such enormous pressure and that is just not happening," she said.
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Next Story


