- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dofetilide comparable to amiodarone for rhythm control in AF patients
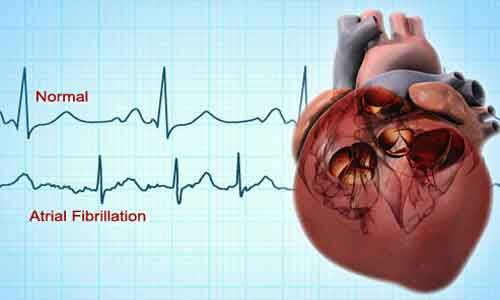
USA: The efficacy of dofetilide (DOF) is as good as amiodarone (AMIO) for rhythm control in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients, finds a recent study in the journal JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The comparative efficacy of DOF versus AMIO in AF patients is not well established. In addition, proarrhythmia has been a concern with DOF therapy. Ghanshyam Shantha, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA, and colleagues aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of dofetilide versus amiodarone in AF patients.
For this purpose, the researchers attempted rhythm control using DOF in 657 consecutive patients with AF (n=528) or atrial flutter and AF (n=129) between January 2014 and December 2018.
Key findings of the study include:
- DOF was successfully initiated in 573 (87%) of 657 patients, including 510 (89%) with persistent AF and 63 (11%) with paroxysmal AF.
- During a mean follow-up of 19 ± 7 months, sinus rhythm was maintained in 361 (63%) of the 573 DOF-treated patients.
- At 12 months, patients on DOF had a similar likelihood of experiencing recurrent atrial arrhythmias compared with the 2,476 consecutive patients treated with AMIO for rhythm control during the study period (37% vs. 39%).
- The efficacy of DOF and AMIO was also similar in specific subgroups of patients, including patients >75 years of age, with a low left ventricular ejection fraction, obesity, renal insufficiency, and prior catheter ablation for AF.
- Among patients with atypical atrial flutter, likelihood of recurrent atrial flutter was similar between the DOF (43 of 108 [40%]) and AMIO (211 of 555 [38%]) groups.
"When properly initiated and monitored, DOF has efficacy comparable to that of amiodarone for rhythm control in patients with AF," concluded the authors.
Reference:
The study titled, "Comparative Efficacy of Dofetilide Versus Amiodarone in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation," is published in the journal JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
DOI: https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacep.2020.11.027
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


